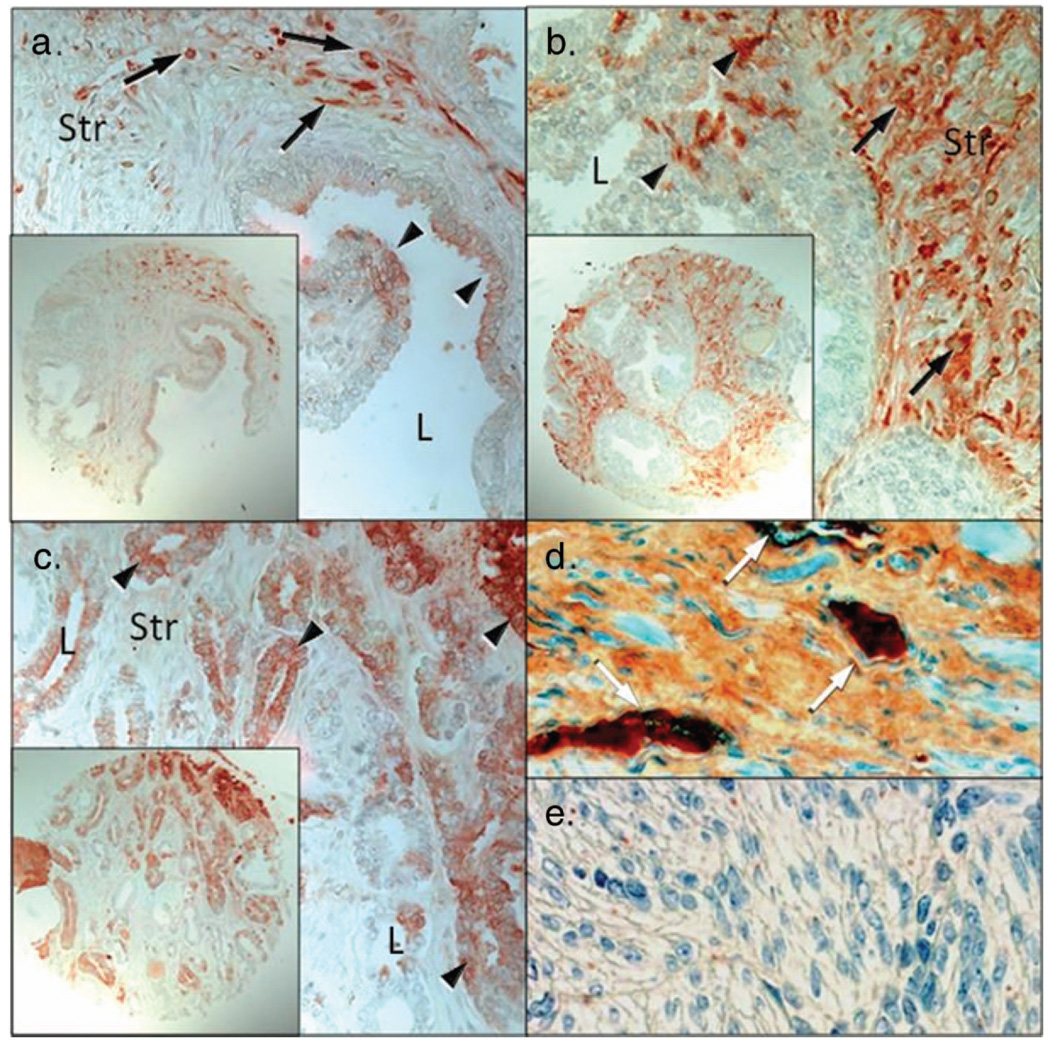
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemical localization of thrombin in normal prostate, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, and prostate cancer specimens. (a) Thrombin protein was localized primarily to prostatic stroma (Str) with little thrombin localized to the epithelium (arrowheads). Arrows denote intense stromal cell positivity within a stromal cell. (b) Localization of thrombin in PIN samples demonstrated increased expression within the stromal layer and little thrombin expression was observed within the epithelium (arrowheads). (c) Localization of thrombin in prostate adenocarcinoma. Prostatic carcinoma cells (arrowheads) whereas stromal cells were diffuse and of moderate intensities for thrombin. (d) prostate specinmen containing thrombin rich vascular (white arrows; positive control). (e) Uterine smooth muscle serves as a negative control (L = lumen; Str = stroma; Bar = 50 µm; insets are at high magnification).