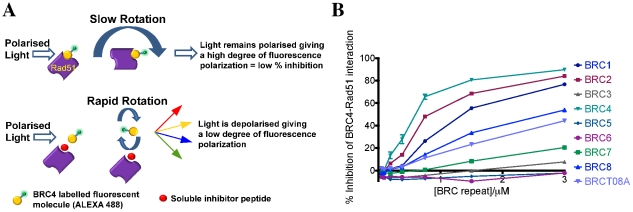
Figure 1. Relative binding affinities of BRC peptides for RAD51 via fluorescence polarisation assays.
a) Principle behind the fluorescence polarisation assay. Alexa-labelled BRC4 peptide rotates slowly when in complex with RAD51 causing polarised light to remain polarised (top panel). Disruption of the BRC4-RAD51 complex by an unlabelled soluble competitor releases the Alexa-labelled BRC4 peptide, which now rotates rapidly causing depolarisation of incoming polarised light (bottom panel). b) Inhibition curves for all eight BRC repeats, as well as the BRC4 T1526A mutant. Full length wild type RAD51 protein was used at a concentration of 135 nM and Alexa488-BRC4 peptide at 10 nM. Peptides able to inhibit the BRC4-RAD51 interaction are detected by a reduction in fluorescence polarisation.