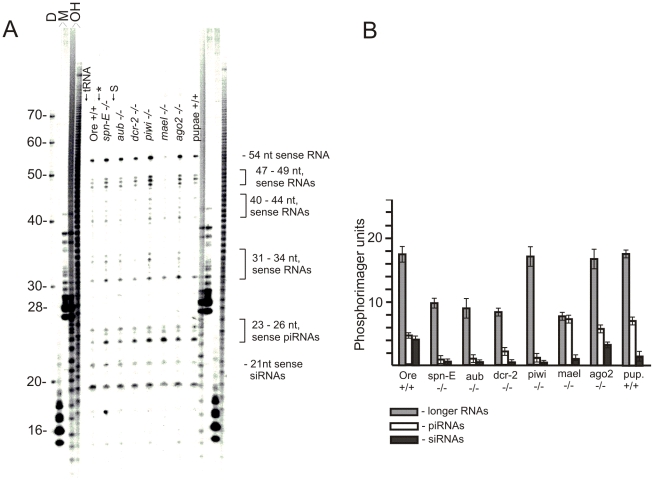
Figure 2. Visualization of a pattern of suffix sense small RNAs from Drosophila ovaries by hybridization with the antisense RNA probe and separation on a high-resolution denaturing acrylamide gel after a nuclease protection assay.
(A) [32P]-labeled gel-purified antisense RNA probe corresponding to the 5′ region of suffix was hybridized overnight with 2–5 µg of total RNA isolated from the ovaries of Oregon R wild-type flies (Ore) or homozygous mutant flies (spn-E, aub, dcr-2, piwi, mael and ago2), with total RNA from pupae or with 5 µg of yeast tRNA. The asterisk indicates results obtained using 5 µg of total Drosophila RNA without hybridization (overnight incubation with the probe at 0°C). S – self-annealing of the probe alone, without any RNA (between spn-E and aub lanes). D – decade RNA marker (Ambion). M – RNA markers, corresponding to RNA synthesized by T7 RNA polymerase on pGEM-1 plasmid templates digested by EcoRI or SmaI enzymes. OH – a partial base-hydrolysis ladder of the gel-purified [32P]-labeled sense RNA probe. The lengths of the RNA molecules (in nt) are as indicated. Sense suffix siRNAs, piRNAs and longer RNAs are indicated by the dash or brackets. (B) Quantification of the separation data. The data shown in panel A were normalized using rp49 as an internal reference. Error bars represent the results obtained in four independent experiments for longer RNAs, piRNAs, and siRNAs.