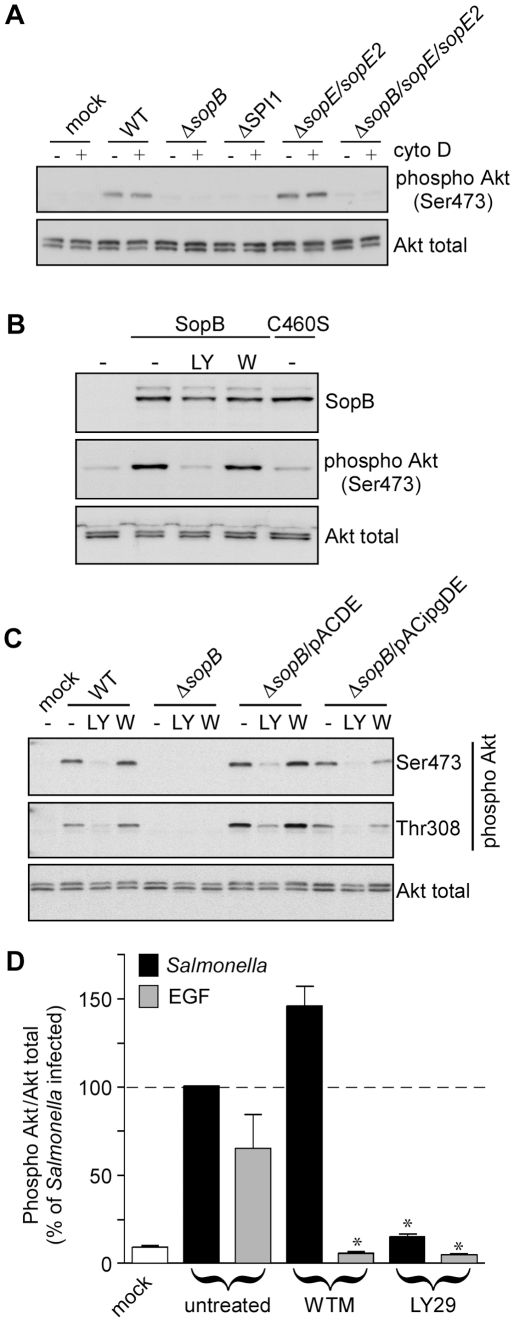
Figure 1. SopB–dependent Akt phosphorylation in epithelial cells is wortmannin insensitive.
(A) HeLa cells were infected with Salmonella, either WT or the indicated mutants, for 20 min. Monolayers were then solubilized in sample buffer and processed for immunoblotting using rabbit polyclonal antibodies to detect phospho Akt (Ser473) and total Akt. Cytochalasin D (cyto D: 1 µg/ml) treated cells were incubated with drug prior to and throughout the infection. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with plasmid expressing 6His-SopB or 6His-SopB C460S for 18 hr. Monolayers were solubilized and processed for immunoblotting using antibodies against SopB, phospho Akt (Ser473) and total Akt. Where indicated, LY294002 (LY: 50 µM) or wortmannin (W:100 nM) were added for 40 min prior to sample collection. (C & D) HeLa cells were treated with EGF (50 ng/ml) for 2 min or infected with Salmonella for 30 min then solubilized and processed for immunoblotting (C) or ELISA (D). To compare the activities of SopB and IpgD the ΔsopB strain was complemented with plasmids pACDE or pACipgDE, respectively. Where indicated cells were pretreated with either LY294002 (LY29: 50 µM) or wortmannin (WTM: 100 nM) for 30 min preceding infection and inhibitor was maintained in the media for all subsequent incubations. Immunoblots are representative from three independent experiments. ELISA data represent means ± SD from three independent experiments (* P<0.05, significantly different from untreated).