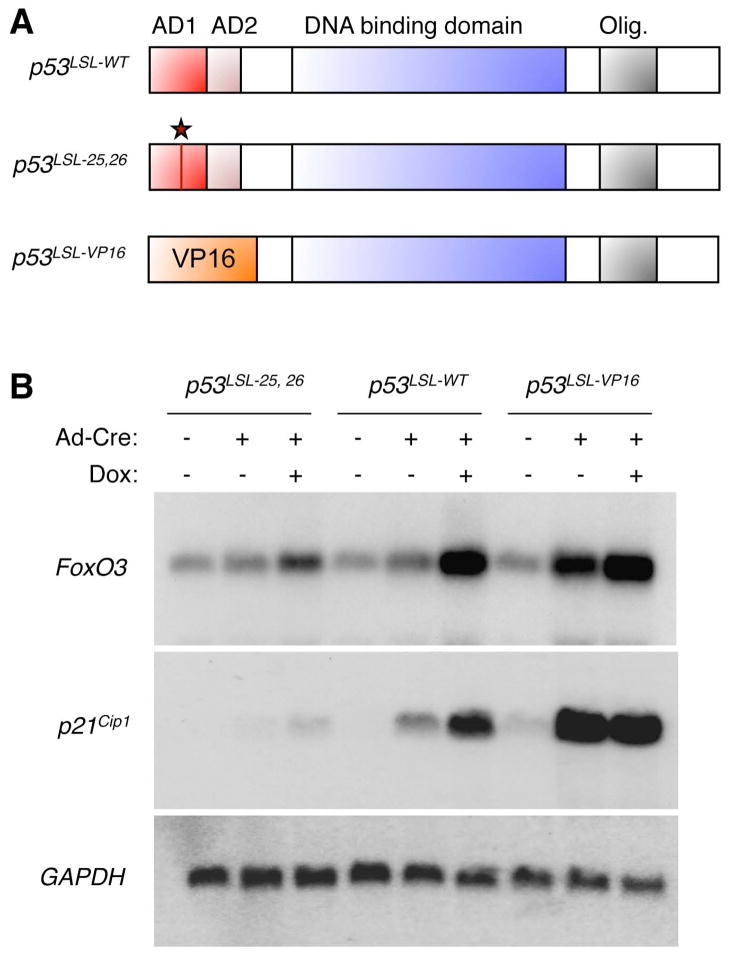
Figure 4. p53 transcriptional activity is necessary and sufficient for FoxO3 mRNA upregulation.
(A) Schematic of the p53 knock-in alleles used. p53LSL-WT: inducible allele encoding a form of wildtype p53. p53LSL-25,26: inducible allele encoding a transcriptionally-impaired mutant of p53 in which leucine 25 is replaced by a glutamine and tryptophan 26 is replaced by a serine. p53LSL-VP16: inducible allele encoding a mutant of p53 in which the transactivation domains (AD1 and AD2) are replaced by the transactivation domain of VP16. AD: activation domain; Olig.: oligomerization domain. The star indicates the location of the 25,26 mutation. (B) Northern-blot analysis of MEFs in which the endogenous allele of p53 has been replaced by an allele encoding inducible forms of WT p53 (p53LSL-WT), a transcription-deficient mutant (p53LSL-25,26), or a mutant of p53 in which the transactivation domains of p53 were replaced by that of VP16 (p53LSL-VP16). The addition of an adenovirus containing Cre recombinase (Ad-Cre) allows the deletion of the Lox-STOP-Lox (LSL) cassette upstream of each allele and allows the expression of each p53 variant. Cells were exposed to 8 hours of doxorubicin (Dox, 0.2 μg/ml). Northern-blots were analyzed with a probe to FoxO3, p21Cip1 (a known target of p53), and GAPDH (loading control).