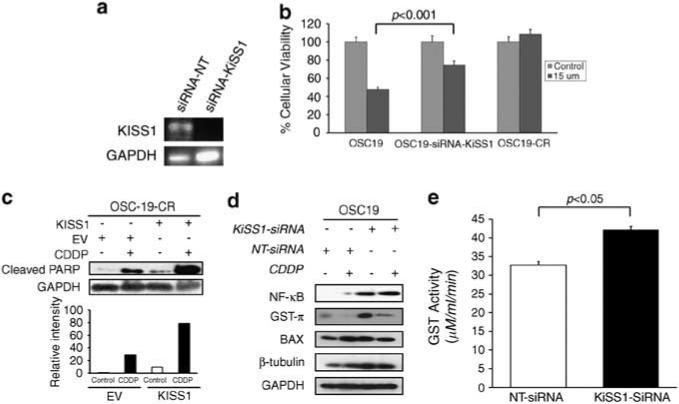
Figure 3.
Genetic knockdown of KiSS1 induces CDDP resistance in HNSCC. (a) Cells were transfected with either an siRNA sequence targeting KiSS1 (siRNA-KiSS1) or a non-targeting siRNA (siRNA-NT). Efficiency of genetic inhibition was determined by PCR. (b) Genetic knockdown of KiSS1 in CDDP-sensitive cells induces CDDP resistance. Depicted cell lines were transfected with the denoted siRNA constructs, exposed to CDDP (15 μm) and then analyzed by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Differences between groups were analyzed by utilizing ANOVA, followed by post hoc comparisons based on Bonferroni's Multiple Comparison Test. Results are reported as mean±s.e.m. A P-value <0.05 was considered significant and all are two-tailed. Experiments were performed in octuplicate and repeated three times. (c) Genetic knockdown of KiSS1 in CDDP-sensitive cells suppresses PARP cleavage. SDS–PAGE was utilized to determine the induction of PARP cleavage in non-targeted siRNA (siRNA-NT)- or KiSS1-targeted siRNA (siRNA-KiSS1)-transfected cells under CDDP treatment conditions (upper panel). Cells were exposed to CDDP for 24 h, lysed and proteins were separated by 10% SDS–PAGE and analyzed for the indicated antibodies. Intensity data depicts suppressed PARP cleavage in siRNA-KiSS1-transfected cells that were exposed to CDDP. Bar graph represents densitometry results. (d) Levels of proteins associated with CDDP sensitivity were analyzed by SDS–PAGE in the depicted cell lines after exposure to CDDP. Increased GST-π expression in the KiSS1-inhibited cells was consistent with the induction of CDDP resistance in the sensitive cell lines. (e) The alteration in GST function was assessed to establish the impact of KiSS1 knockdown in CDDP-sensitive cells. Specific GST activity is expressed on the y axis and was calculated dividing the absorbance change per minute with the extinction coefficient for CDNB (A = 9.6 per mm) and the total protein content of the cell homogenate. Results are reported as mean±s.e.m. A P-value <0.05 was considered significant, and all are two-tailed. Experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated three times. A full colour version of this figure is available at the Oncogene journal online.