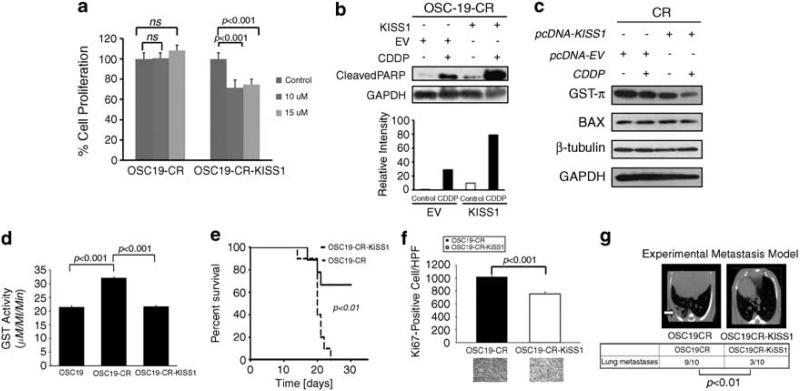
Figure 5.
Re-expression of KiSS1 reverses the CR phenotype in vitro and in vivo. (a) Empty-vector- or KiSS1-tranfected cells were treated with depicted concentrations of CDDP and assessed for cellular proliferation after 24 h of exposure. Differences between groups were analyzed by utilizing ANOVA, followed by post hoc comparisons based on Bonferroni's Multiple Comparison Test. Results are reported as mean±s.e.m. A P-value <0.05 was considered significant, and all are two-tailed. Experiments were performed in octuplicate and repeated three times. (b) SDS–PAGE was utilized to determine the induction of PARP cleavage in mock-transfected or KiSS1-tranfected CR cells under CDDP treatment conditions (upper panel). Cells were exposed to CDDP for 24 h, lysed and proteins were separated by 10% SDS–PAGE and analyzed for the indicated antibodies. Intensity data depicts relative increase in PARP cleavage in CDDP-treated KiSS-overexpressing cells. (c) Levels of proteins associated with CDDP-resistant were analyzed by SDS–PAGE in the depicted cell lines after exposure to CDDP. Reduced GST-π expression in the KiSS1-expressing cells was consistent with the re-establishment of CDDP sensitivity in CR cells. (d) The alteration in GST function was assessed to establish the impact of KiSS1 overexpression in the CR cells. Specific GST activity is expressed on the y axis and was calculated dividing the absorbance change per minute with the extinction coefficient for CDNB (A = 9.6 per mm) and the total protein content of the cell homogenate. Results are reported as mean±s.e.m. A P-value <0.05 was considered significant, and all are two-tailed. Experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated three times. (e) OSC19-CR cells transfected with either an empty vector (OSC19CR) or a KiSS1 overexpression construct (OSC19CR-KiSS1) were injected into the tongues of nude mice. Mice were then observed and killed when moribund. (f) Mice harboring orthotopically implanted OSC19CR-KiSS1 tumors (n = 7) had improved survival compared to those with OSC10CR tumors (n = 6), as determined by the Kaplan–Meier method. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Immunohistochemical analysis of Ki67 revealed statistically significant decrease in cellular proliferation in the KiSS1-tranfected CR tumors compared with the CR tumors (P<0.001). (g) After injection into the tail vein, mice were monitored for the development of pulmonary metastasis with micro-computed tomography imaging (OSC19CR, n = 10; OSC19CR-KiSS1, n = 10). After 6 weeks, mice were killed and the lungs of all mice were examined both grossly and microscopically for pulmonary metastasis. Differences between the number of lung metastases per group were evaluated by the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. Representative micro-computed tomography images are shown. Results are reported as mean±s.e.m. Results are representative of three independent experiments. A full colour version of this figure is available at the Oncogene journal online.