Table 1.
Summary of different polymeric families’ applications, advantages, disadvantages, degradation rate and structure.
| Polymer | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages | λ, Degradation Rate Constant (s−1) | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyphosphazenes | Tissue Engineering Vaccine Adjuvant |
Synthetic Flexibility Controllable Mechanical Properties |
Complex Synthesis | 4.5 × 10−2 −1.4 × 10−7 Ref. 776,13 |
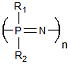
|
| Polyanhydrides | Drug Delivery Tissue Engineering |
Significant Monomer Flexibility Controllable Degradation Rates |
Low Molecular Weights Week Mechanical Properties |
1.9 × 10−3 − 9.4 × 10−9 Ref. 17,777 |
|
| Polyacetals | Drug Delivery | Mild pH Degradation Products pH Sensitive Degradation |
Low Molecular Weights Complex Synthesis |
6.4 × 10−5 Ref. 17 |
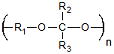
|
| Poly(ortho esters) | Drug Delivery | Controllable Degradation Rates pH Sensitive Degradation |
Week Mechanical Properties Complex Synthesis |
4.8 × 10−5 Ref. 17 |
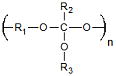
|
| Polyphosphoesters | Drug Delivery Tissue Engineering |
Biomolecule Compatibility Highly Biocompatible Degradation Products |
Complex Synthesis | 1.4 × 10−6 Ref. 778,779 |
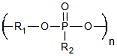
|
| Polycaprolactone | Tissue Engineering | Highly Processable Many Commercial Vendors Available |
Limited Degradation | 3.5 × 10−8 Ref. 17 |
|
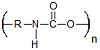
| Polyurethanes | Prostheses Tissue Engineering |
Mechanically Strong Handle Physical Stresses Well |
Limited Degradation Require Copolymerization with Other Polymers |
8.3 × 10−9 Ref. 780 |
|
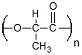
| Polylactide | Tissue Engineering Drug Delivery |
Highly Processable Many Commercial Vendors Available |
Limited Degradation Highly Acidic Degradation Products |
6.6 × 10−9 Ref. 17 |
|
| Polycarbonates | Drug Delivery Tissue Engineering Fixators |
Chemistry-Dependent Mechanical Properties Surface Eroding |
Limited Degradation Require Copolymerization with Other Polymers |
4.1 × 10−10 Ref. 285 |
|
| Polyamides | Drug Delivery | Conjugatable Side Group Highly Biocompatible Degradation Products |
Very Limited Degradation Charge Induced Toxicity |
2.6 × 10−13 Ref. 17 |
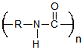
|
