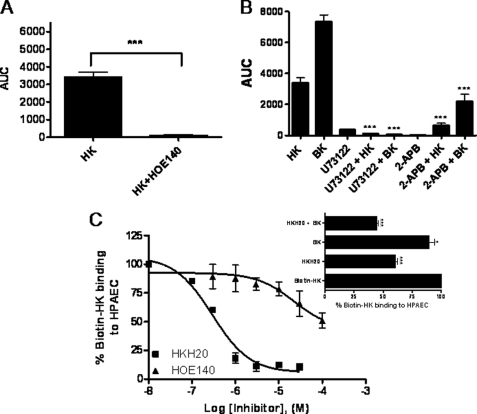
FIGURE 3.
HK activates bradykinin B2 receptors on HPAEC. Panel A, effect of HOE140 on HK-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. Panel A, HPAEC were treated with HK (300 nm) in the absence or presence of HOE140 (1 μm). Changes in [Ca2+]i levels in cells were measured using a Zeiss LSM 510 META confocal microscope at an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and an emission wavelength of 505 nm and the expressed as area under curve. Data are presented as mean ± S.E. Panel B, effect of U73122 and 2-APB on HK-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. HPAEC were treated with HK (300 nm) in the absence or presence of U73122 (5 μm) or 2-APB (100 μm). Changes in [Ca2+]i levels in cells were measured as described in panel A. Data are presented as mean ± S.E. Panel C, effect of HKH20, HOE140 and BK on biotin-HK binding to HPAEC. HPAEC (4 × 104 cells/well) were incubated with biotin-HK (20 nm) in the absence or presence of increasing concentration of HKH20 (0.1–30 μm) or HOE140 (0.3–100 μm) for 1 h at 37 °C. The binding of biotin-HK to cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate and peroxide specific fast-reacting substrate turbo-TMB. The reaction was stopped by adding 1 m phosphoric acid (100 μl) and the level of binding was determined by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture in each well at OD 450 nm. Inset, effect of BK and HKH20 + BK on biotin-HK binding to HPAEC. HPAEC (4 × 104 cells/well) were treated with biotin-HK (20 nm) in the absence or presence of HKH20 (0.3 μm), BK (0.5 mm), or HKH20 (0.3 μm) + BK (0.5 mm) and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. Biotin-HK binding was determined as described in panel C. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001.