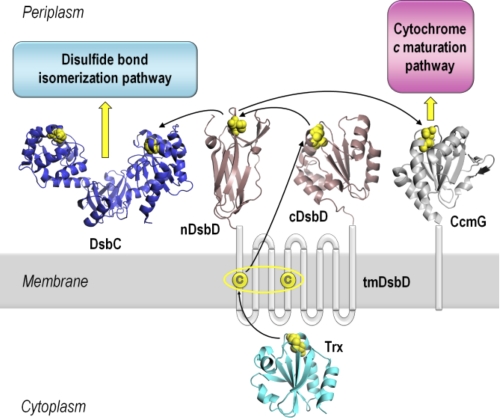
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of DsbD and its interacting partners. DsbD has three domains, a central hydrophobic domain with eight transmembrane helices (tmDsbD) and two periplasmic globular domains (nDsbD and cDsbD). The proposed pathway of electron flow from thioredoxin (Trx) in the cytoplasm, via the three domains of DsbD, to the Ccm and disulfide bond isomerization pathways in the periplasm is shown. Trxred reduces the disulfide bond in tmDsbDox, and tmDsbDred then reduces cDsbDox, which then reduces nDsbDox. DsbC, a dimeric disulfide isomerase, and CcmG, a component of the Ccm system, then accept reductant from nDsbDred. The pairs of conserved cysteines that form disulfide bonds are shown in yellow. The structures shown are from the following PDB entries: nDsbD (1JPE (16)), cDsbD (2FWF (21)), Trx (2TRX (53)), DsbC (1EEJ (54)), CcmG (2B1K (55)). All structures were rendered in PyMOL (56).