FIGURE 2.
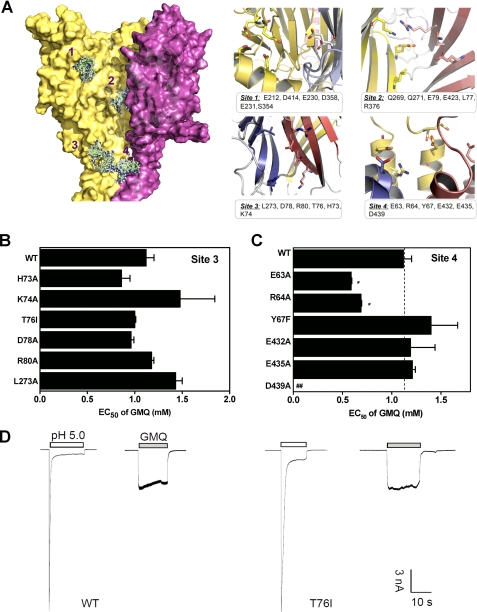
Potential binding sites of GMQ in the three-dimensional ASIC3 model. A, structure and key residues (displayed in sticks for emphasis) of potential binding sites of GMQ. The potential binding sites were detected using cavity searching algorithm encoded in Discovery Studio®, version 2.1. GMQ was docked into the potential binding site of ASIC3 using docking program Glide (version 4.0; Schrödinger). B and C, EC50 values of GMQ (means ± S.E., n = 3–10) for point mutations in Sites 3 (B) and 4 (C). In C, the WT EC50, taken from B, is regraphed again for comparison. *, p < 0.05 versus WT ASIC3 (dashed line). D, examples of GMQ-evoked (1 mm) currents at neutral pH in WT and mutated ASIC3 channels (as exemplified by T76I). Similar results were obtained in four other experiments.