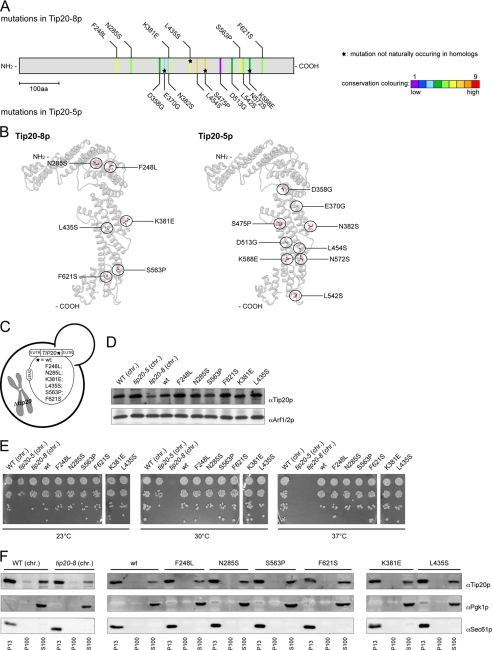
FIGURE 1.
Analysis of Tip20-5 and Tip20-8 mutants. A, sequencing of the tip20-5 and the tip20-8 alleles revealed nine and six amino acid (aa) changes, respectively. An alignment and evaluation of evolutionarily conserved residues for Tip20p was performed using the ConSurf database (41). The conservation scores were normalized and translated to nine color codes, which represent the grade of conservation; 1 is maximum variability and 9 is maximum conservation. The mutations occurring in Tip20-8p (top) and in Tip20-5p (bottom) were mapped onto the linear sequence. Stars indicate mutations that do not occur naturally in sequences of TIP20 homologues in other species. Neither the mutations found in tip20-8 nor the ones identified in tip20-5 cluster on the linear sequence. B, the mutations in Tip20-8p and Tip20-5p are relatively evenly distributed throughout the protein, with some enrichment along the α-helical stalk region of the protein. Mutations occurring in Tip20-8p (left) and in Tip20-5p (right) were incorporated into the x-ray crystal structure of Tip20p (3FHN) using the mutation tool in the Swiss-pdb Viewer (44). The side chain conformations of the mutated residues were regenerated from the backbone structure using the program SCWRL (45). C, schematic drawing of yeast strains expressing variants of Tip20p that contain only one of the mutations identified in tip20-8. D, all single point mutation constructs express Tip20p to a similar extent than the wild-type constructs. Immunoblots of protein extracts from the single point mutation were performed. Detection of Arf1/2p was used as loading control. chr., the chromosomally encoded TIP20 versions. E, none of the single point mutations showed any growth defect at any tested temperature. Growth assays were performed at the indicated temperatures to test the tip20 mutant strains. The tip20-8 strain displays a growth defect at 30 °C and above, whereas the tip20-5 strain only ceases to grow at 37 °C. F, in all strains, most of Tip20p was found in the P13 fraction, which contains mostly ER membranes. A smaller portion of Tip20p was found in the S100 fraction. Subcellular fractionations of the indicated strains were performed and analyzed by immunoblots. Pgk1p was used as a marker for cytosolic proteins, whereas Sec61p served as a marker for ER membranes.