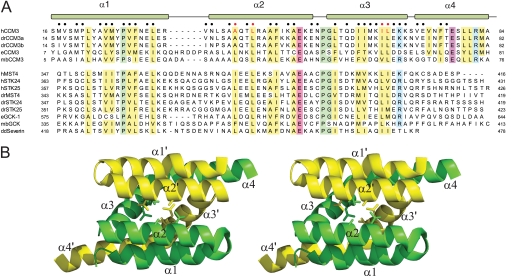
FIGURE 2.
Sequence conservation between CCM3 and GCKIII proteins. A, sequence alignment of CCM3 N-terminal and GCKIII protein C-terminal tails regions. h, human; dr, Danio rerio; e, C. elegans; mb, Monosiga brevicollis; and dd, Dictyostelium discoidium sequences of CCM3 and GCKIII proteins (STK24, MST4, STK25, and severin) are shown. Conserved hydrophobic, acidic, basic, and proline/glycine residues are highlighted in yellow, red, blue, and green, respectively. Residues comprising the CCM3 homodimer interface are indicated by circles (●) at the top of the alignment. The CCM3 residues (Leu-44, Ala047, Ile-66, and Leu-67) mutated in this study are highlighted with red circles. B, schematic of the N-terminal dimerization region of CCM3 (Protein Data Bank code 3L8I). Protomer chains are colored yellow and green with residues mutated in this study shown in stick representation. Secondary structure elements are labeled.