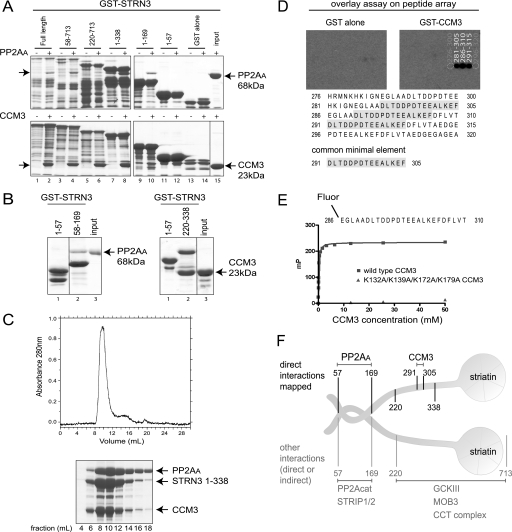
FIGURE 2.
Striatin binds directly to PP2AA and CCM3. A, mapping of the direct in vitro association between GST-STRN3 truncation mutants and PP2AA (top) or CCM3 (bottom). Bacterially expressed and purified GST-STRN3 deletion proteins were used for GST pulldown assays with soluble PP2AA or CCM3; GST alone was used as a negative control. Proteins were visualized by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. The soluble proteins were added to even numbered lanes only. The position of the soluble proteins are indicated by arrows. B, amino acids 58–169 of GST-STRN3 are sufficient to mediate an interaction with PP2AA (left) and amino acids 220–338 are sufficient to mediate the interaction with CCM3 (right) in a GST pulldown assay. GST-STRN3(1–57) was used as a negative control. C, PP2AA, STRN3(1–338), and CCM3 form a complex that is stable throughout the course of gel filtration. Bacterially expressed recombinant proteins were purified and loaded onto a Superdex 200 gel filtration column. The proteins elute as one major peak, ∼8–12 ml, as detected by A280 nm (top) and SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie staining (bottom). D, peptide array identifies the core STRN3 residues (amino acids 291–305) responsible for binding to GST-CCM3 in an overlay assay. 25-mer peptides derived from STRN3(220–338) were spotted on a membrane (see supplemental Fig. 3 for Coomassie staining of the membrane) and subjected to an overlay assay with GST-CCM3 (or GST alone) followed by detection with anti-GST and horseradish peroxidase-coupled secondary antibodies. The sequence of the common minimal element from the peptides that display association is highlighted. E, fluorescence polarization indicates that a fluorescent 25-mer STRN3 peptide (amino acids 286–310) interacts with wild-type CCM3. The minimal sequence of STRN3 determined in D, plus five flanking residues on either side, was synthesized as a fluorescent peptide and used in a fluorescence polarization assay. This peptide readily interacts with wild-type CCM3 (blue curve). However, substitution of Lys-132, Lys-139, Lys-172, and Lys-179 in CCM3 for alanines completely abrogated association with the STRN3 peptide (see Fig. 3 for description of this mutant). F, summary of the binding surfaces mapped on striatin (results from Figs. 1 and 2).