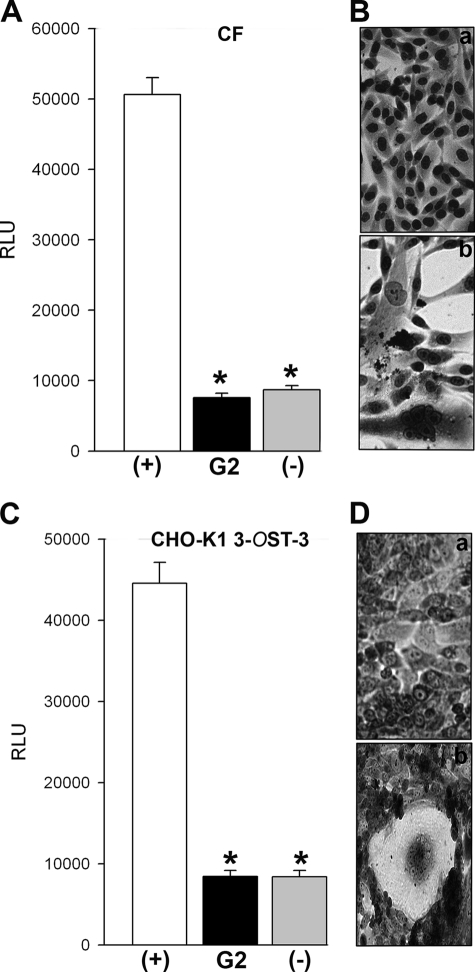
FIGURE 7.
Effect of G2 on HSV-1 glycoprotein induced cell-to-cell fusion and spread. A, the effector CHO-K1 cells expressing HSV-1 glycoproteins (B, D, H–L, and T7 polymerase) were preincubated with G2 peptide (black bar) or 1 × PBS (white bar) (+) for 90 min. Control effector cells (T7 polymerase and glycoproteins gD, H–L only) (−) were also preincubated with G2 for the same duration. The effector cells were then mixed with primary cultures of human corneal fibroblasts (panels A and B) or 3-OST-3-expressing CHO-K1 cells (panels C and D) transfected with luciferase gene under T7 control. Membrane fusion as a surrogate for viral spread was detected by monitoring luciferase activity (panels A and C). Relative luciferase units (RLUs) were determined using a Sirius luminometer (Berthold detection systems). Error bars represent S.D. *, p < 0.05, one way analysis of variance. Microscopic images of Giemsa (Fluka)-stained polykaryocytes show the preventative effect of G2s on cell fusion (panels B and D). Shown above are 40× magnified photographs of cells undergoing membrane fusion (Zeiss Axiovert 200).