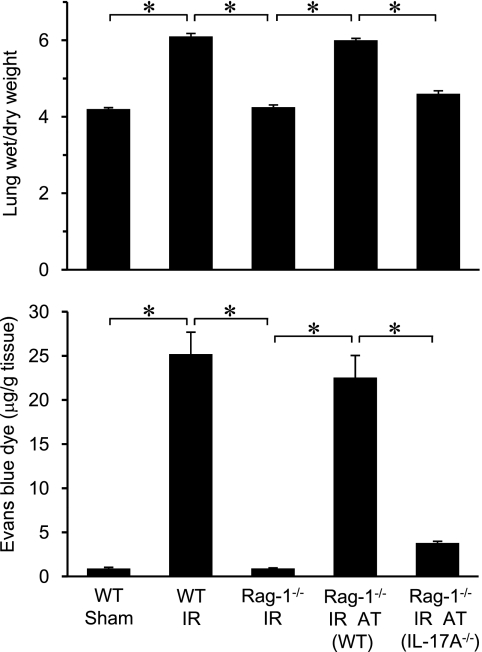
Figure 4.
CD4+ T-cell–derived IL-17A mediates lung injury after ischemia–reperfusion (IR). Lung injury was assessed by measuring pulmonary edema (via lung wet/dry weight) and vascular permeability (via Evans blue dye extravasation). Wild-type (WT) and Rag-1−/− mice with or without adoptive transfer (AT) of CD4+ T cells from WT or IL-17A−/− mice were assessed (n = 5/group). Pulmonary edema and vascular permeability were significantly elevated in lungs of WT mice after IR compared with sham, which was blocked in Rag-1−/− mice. Adoptive transfer of CD4+ T cells from WT mice, but not IL-17A−/− mice, restored pulmonary edema and vascular permeability after IR in Rag-1−/− mice. *P < 0.001.