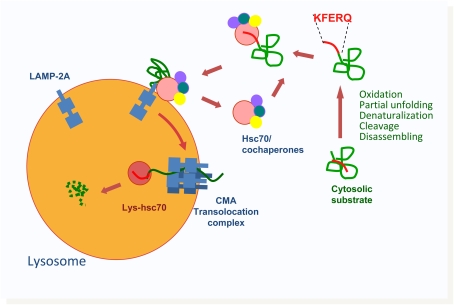
Figure 3.
Schematic model of chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). Cytosolic proteins substrate for CMA can undergo different modifications that lead to the exposure of the CMA-targeting motif and its subsequent recognition by cytosolic heat shock protein of 70 kD (Hsc70). The complex between the substrate protein, hsc70, and its cochaperones is delivered to the surface of the lysosomal membrane, where it interacts with lysosome-associated membrane protein (LAMP)-2A, the receptor for CMA. Once bound to LAMP-2A, substrate proteins undergo complete unfolding, and, assisted by a luminal form of hsc70 (Lys-hsc70), they cross the lysosomal membrane for rapid degradation in the lumen.