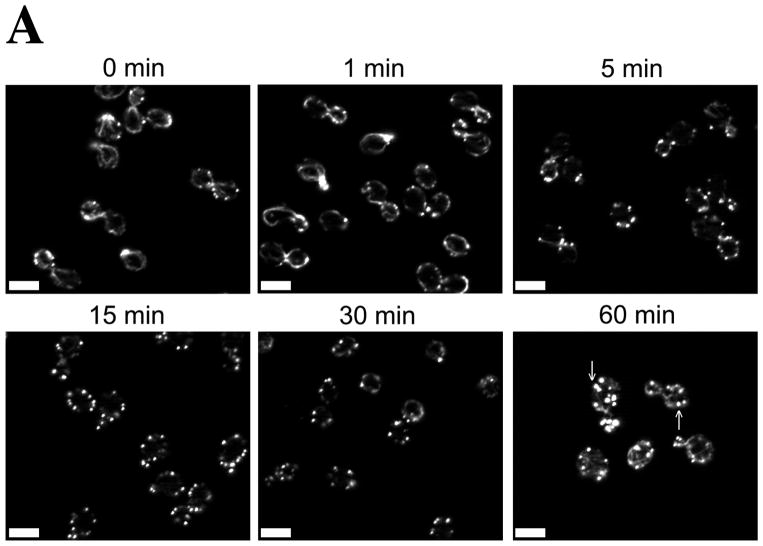
Figure 1. Centrally located Oxidized Actin Bodies (OABs) form rapidly after hydrogen peroxide treatment.
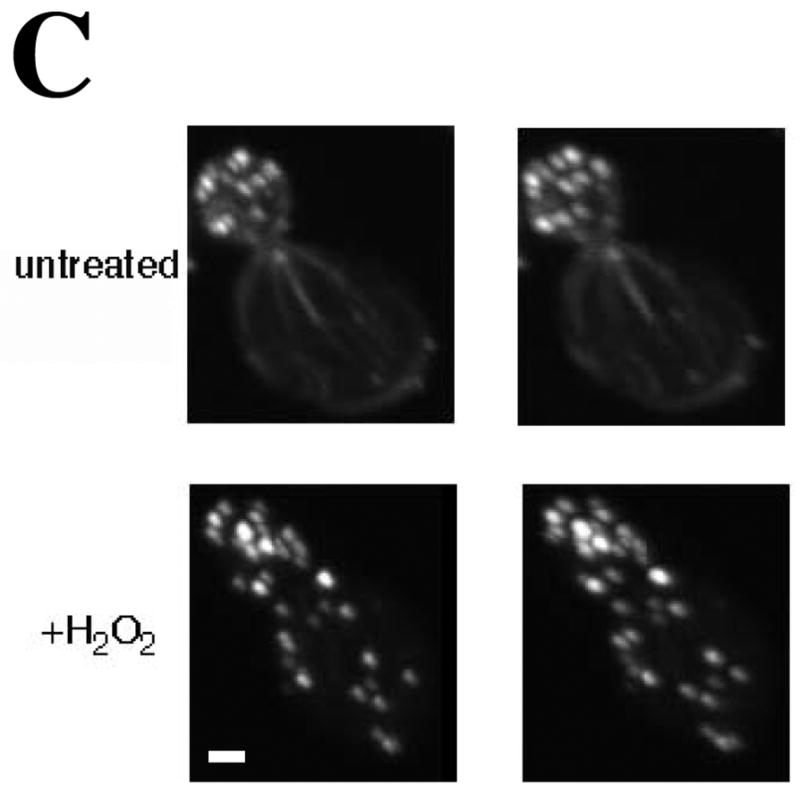
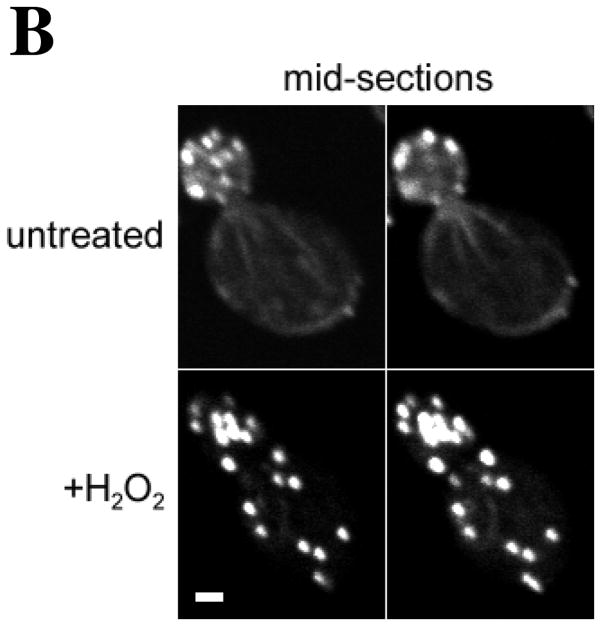
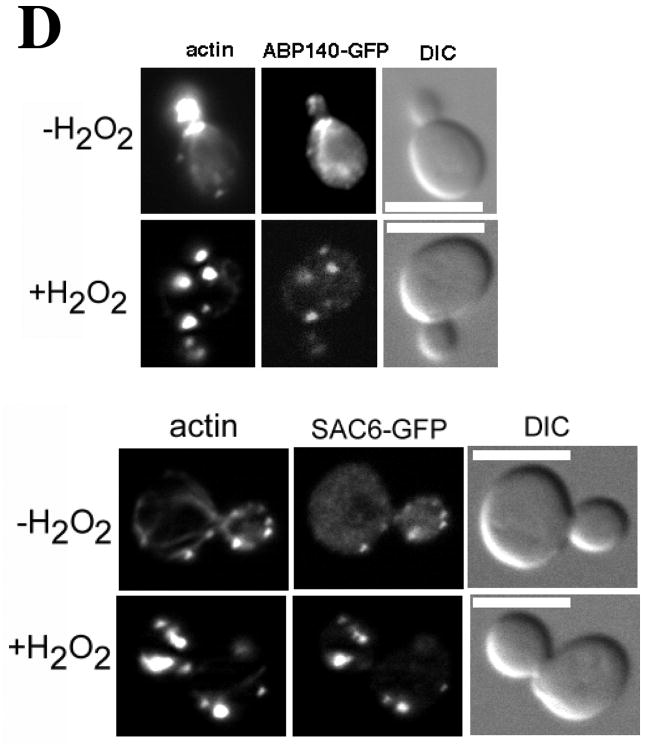
(A) Time course of OAB formation. Cells were treated with 2.9 mM H2O2 and at the indicated times, fixed and stained with rhodamine-phalloidin. Arrows indicate OABs. Scale bars, 5 μm. (B) Central Z-sections 12 (left) and 13 (right) from a total of 25 sections that were collected at 0.3 μm intervals from cells untreated or treated for 1 h with 2.9 mM H2O2. Scale bar, 1 μm. (C) Stereo image pairs of the cells shown in (B) generated from 3D reconstructions made from Z-stacks spanning the entire cell depth. Scale bar, 1 μm. (D) Co-localization of Apb140p and Sac6p with actin in OABs. Cells expressing GFP fusions to Abp140p and Sac6p were treated with 2.9 mM H2O2 for 1 h, fixed for 10 min and stained with rhodamine-phalloidin. Scale bars, 5 μm.