Figure 5.
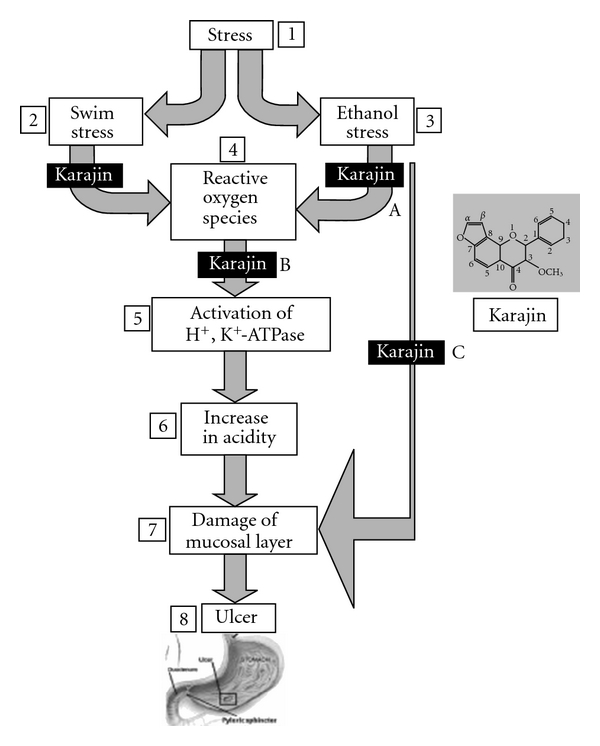
Mechanism of ulcer induction; multi-step protection by karanjin. In stress (1)–swim (2)/ethanol (3) model, ulcer (8) induction is via accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (4), activation of H+, K+-ATPase (5), increase in acidity (6) and damage of mucosal layer (7) while, in ethanol stress, it is more direct and via damage of mucosal layer due to lack of microcirculation. Karanjin protects multi-steps which includes inhibition of ROS (A), inhibition of H+, K+-ATPase (B) and mucosal protection (C). It is also possible that karanjin, like most of the phenolics, may just regulate proton pump via dehydrogenase coupling.
