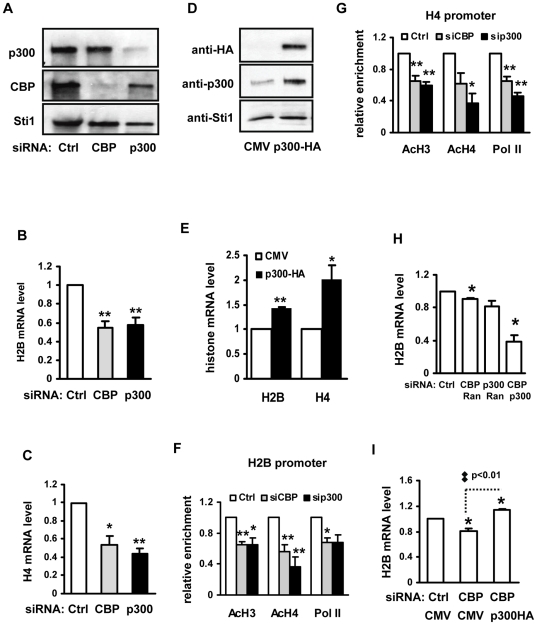
Figure 2. CBP and p300 are required for histone gene expression and histone acetylation on histone promoters.
In A–C, F and G, HeLa cells were transfected with 100 nM of CBP or p300 specific siRNA with random siRNA as control (Ctrl). For D and E, HeLa cells were transfected with 3 µg/ml of p300-HA encoding plasmids or empty vector CMV. Cells were harvested for Western-Blot, RT-qPCR or ChIP analysis 48 hours post transfection. (A) The specificity and efficiency of the knockdown of CBP and p300. Western-Blot was performed with rabbit anti-p300, mouse anti-CBP or rabbit anti-Sti1 antibody as indicated. Sti1 (Stress-inducible protein 1) level was used as a loading control. (B) Decreased H2B expression in CBP or p300 knockdown cells. n = 5. (C) Decreased H4 expression in CBP or p300 knockdown cells. n = 5. (D) Over-expression of HA-tagged p300. (E) Increased H2B and H4 expression in p300 over-expressing cells. n = 3. (F) Reduced level of acetylated H3, H4 and RNAPII at the H2B promoter by CBP or p300 knockdown. n = 5. (G) Reduced level of acetylated H3, H4 and RNAPII at the H4 promoter by CBP or p300 knockdown. n = 4. (H) The additive effect of double knockdown of CBP and p300. HeLa cells were transfected with 50 nM of CBP and/or p300 specific siRNA; compensating dosage of random siRNA was used to make the concentration of total siRNA at 100 nM, n = 3. (I) Compensation of reduced H2B expression resulted from CBP knockdown by p300 over-expression. Comparison between column 2 and 3 was analyzed with unpaired t test. n = 3.