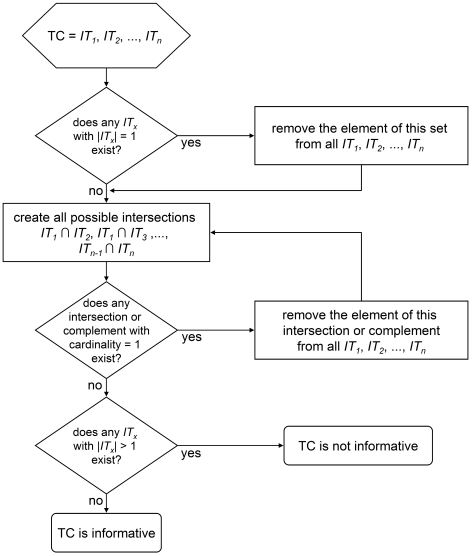
Figure 1. Test for informativeness.
Each infection type is considered as a set with the Wolbachia strains as its elements. All sets are checked for having a cardinality of 1. If such a set is identified, the element contained in it subtracted from all sets. Next, all possible pairs of sets are explored for intersections or complements with a cardinality of 1. If found, the contained element is subtracted from all sets and the exploration of all possible remaining pairs is repeated until no intersection or complement with a cardinality of 1 can be identified. If the cardinality of the largest remaining set is >1, the type combination is not informative; otherwise the type combination is informative and allows complete allele assignment.