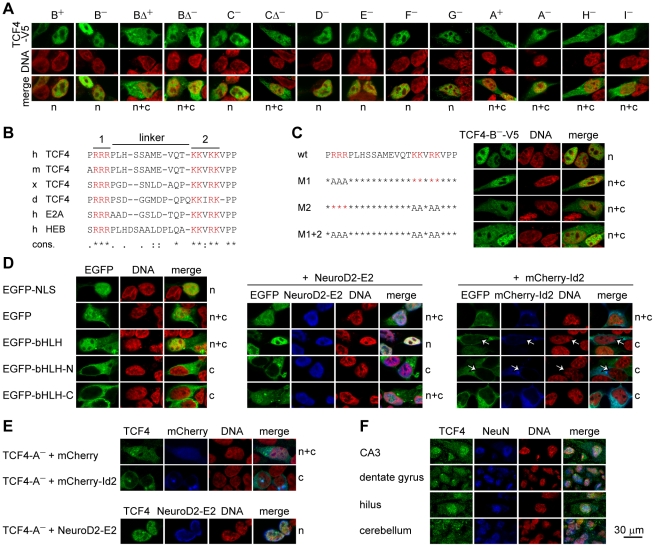
Figure 6. TCF4 intracellular localization.
(A) Immunocytochemical analysis of V5-tagged TCF4 isoforms overexpressed in HEK293 cells. Isoforms analyzed are indicated at the top and localization pattern at the bottom of the panel. n, nuclear; c, cytoplasmic; n+c, nuclear and cytoplasmic. DNA was counterstained with DAPI (pseudocoloured red) to visualize nuclei. (B) Alignment of the identified bipartite NLS in TCF4 of Homo sapiens (h), Mus musculus (m), Xenopus laevis (x) and Danio rerio (d); in E2A and HEB of Homo sapiens. Two clusters of basic amino acids (in red, 1 and 2) and the linker are indicated with lines at the top. Conservation is indicated at the bottom. ‘*’, identity; ‘:’, conserved; ‘.’, semi-conserved substitution. (C) The effect of site-directed mutagenesis of the NLS on the localization of TCF4 in HEK293 cells. Basic amino acids in cluster 1 (M1), 2 (M2) or both (M1+2) were replaced with alanines in the context of TCF4-B−-V5 and the localization of the proteins was monitored by immunocytochemistry. (D) Localization of EGFP fusion proteins with TCF4 NLS, bHLH, N-terminal (N) or C-terminal (C) half of TCF4 bHLH domain in HEK293 cells. NeuroD2-E2 or mCherry-Id2 encoding plasmid was cotransfected when indicated. White arrows indicate cells expressing mCherry-Id2. (E) Effect of mCherry-Id2 or NeuroD2-E2 co-expression on subcellular distribution of TCF4-A−. The localization patterns of overexpressed TCF4 proteins are indicated at the right of the panels in C, D and E. (F) Immunohistochemical analysis of endogenous TCF4 in human hippocampal and cerebellar sections. NeuN staining was used to identify neurons.