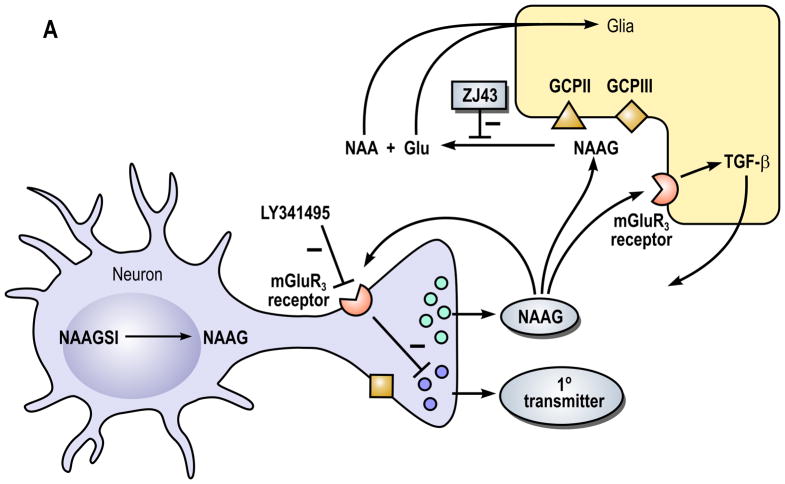
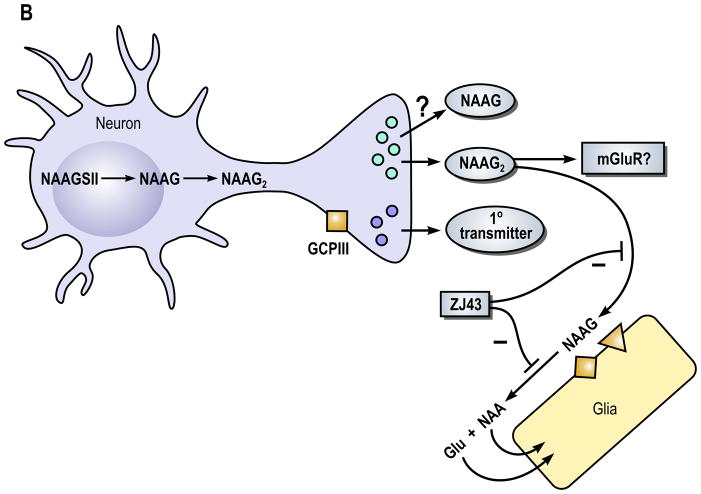
Figure 1. A model of the role of N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) peptidase inhibition and its influence on (A) NAAG and (B) N-acetylaspartylglutamylglutamate (NAAG2) in the nervous system.
In part A, the neuron expresses NAAG synthetase I (NAAGS I), an enzyme that mediates the synthesis of NAAG but not NAAG2. In this cell, NAAG is co-released with a primary amine transmitter, such as glutamate, under conditions of elevated neuronal activity. While the primary transmitter is released into the immediate synaptic space, the peptide is released perisynaptically where it activates presynaptic and glial type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR3). NAAG is inactivated by glutamate carboxypeptidases II (GCPII) and III (GCPIII), forming N-acetylaspartate (NAA) and glutamate (Glu), which are transported into glial cells. While GCPIII is expressed by neurons and glia in cell culture (Bzdega et al., 2004), its localization on presynaptic ending is purely speculative. High levels of glutamate-mediated neurotransmission are associated with several clinical disorders including traumatic brain injury, stroke, peripheral neuropathy, inflammatory pain and schizophrenia. NAAG inhibits glutamate release by activation of presynaptic mGluR3 receptors. Inhibition of the peptidases GCPII and GCPIII by a NAAG peptidase inhibitor, such as ZJ43, reduces inactivation of NAAG. In animal models of these disorders, the NAAG peptidase inhibitor-mediated elevation of peptide levels increases the activation of mGlu3 receptors on axon endings, inhibiting further glutamate release and reducing the pathology. In a second neuroprotective pathway, NAAG activation of mGlu3 receptors on glial cells stimulates the release of a trophic factor, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β).
In Part B, the neuron expresses NAAG synthetase II (NAAGSII), an enzyme that mediates the synthesis of NAAG and NAAG2. In this model, we propose that NAAG2 and perhaps NAAG are co-released with a primary amine transmitter, again as it the case for other neuropeptides, under conditions of elevated neuronal activity. The receptor that NAAG2 might activate has not been identified but is likely to be defined in the near future. Since GCPII hydrolyzes both NAAG and NAAG2, peptidase inhibitors such as ZJ43 can be predicted also to elevate levels of NAAG2 and increase its activity.