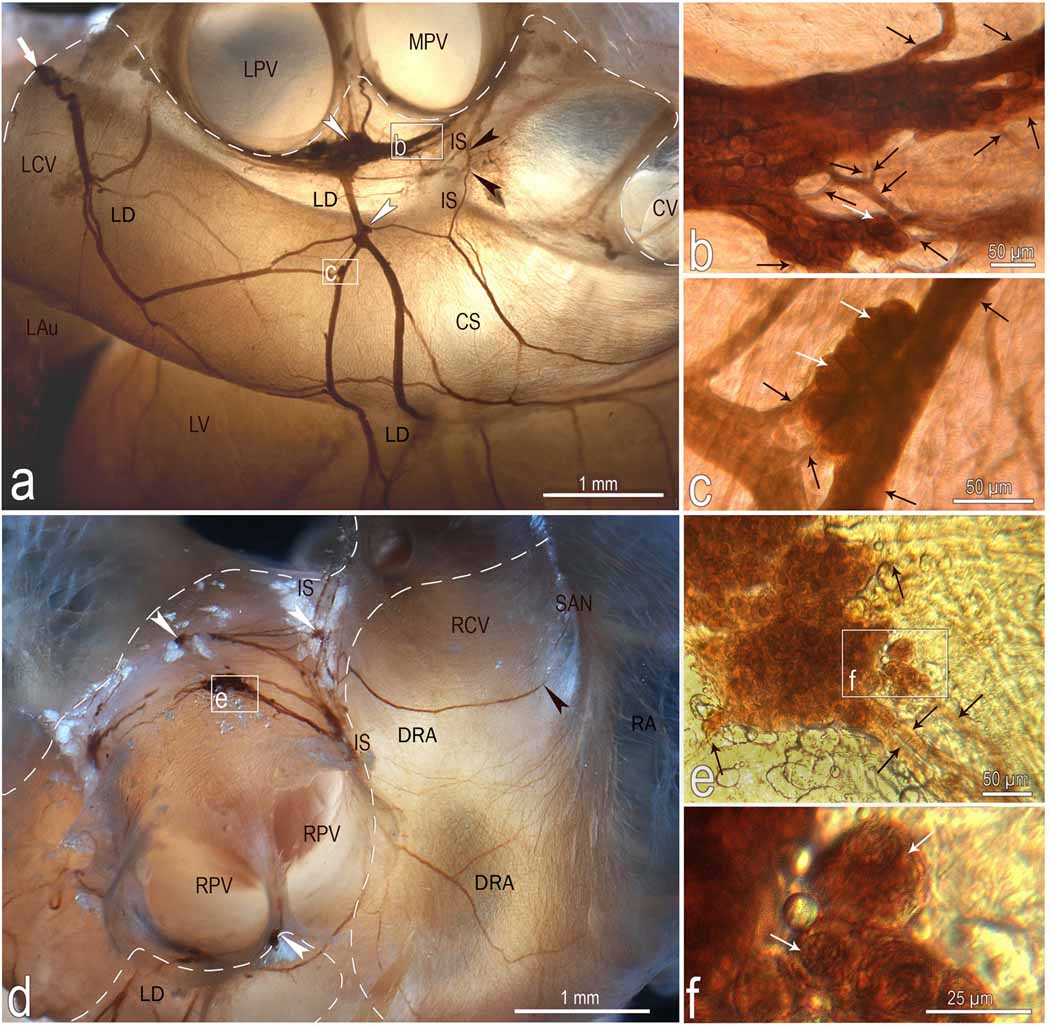
Fig 3.
Location, course and structure of left dorsal (LD) and dorsal right atrial (DRA) neural subplexuses in a mouse heart stained histochemically for acetylcholinesterase. Boxed areas b and c in a, e in d and f in e were enlarged using a contact microscope and shown respectively as b, c, e, and f insets. Black arrowheads in a point to the nerves that penetrate into interatrial septum, while in d one that proceeds toward the region of the sinuatrial node (SAN). White arrowheads, some ganglia; white solid arrows, nerves entering the ganglionated nerve plexus of the heart hilum; Black thin arrows, interganglionic nerves, white thin arrows, some neurons. Dashed line limits the heart hilum. In d, note the right ganglia situated at the root of right cranial vein on the interatrial groove. Other abbreviations: CS – coronary sinus; CV – orifice of caudal (inferior caval) vein; IS – interatrial groove; LAu – inferior surface of left auricle; LCV – left cranial vein; LPV – orifice of left pulmonary vein; LV – left ventricle; RA – right atrial wall; MPV – orifice of middle pulmonary vein; RPV – orifice of right pulmonary vein; RCV – root of right cranial (superior caval) vein.