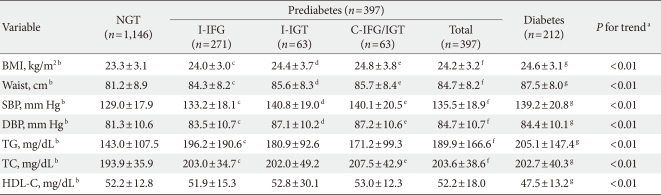
Table 4.
Associated metabolic risk factors according to diagnostic criteria (n=1,755)
NGT, normal glucose tolerance; I-IFG, isolated impaired fasting glucose; I-IGT, isolated impaired glucose tolerance; C-IFG/IGT, combined impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance; BMI, body mass index; Waist, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; TG, triglyceride; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol.
a"P for trend" was used to compare normal, prediabetes, and diabetes groups, bExpressed as mean±SD, cSignificant difference of normal/isolated impaired fasting glucose (P<0.05), dSignificant difference of normal/isolated impaired glucose tolerance (P<0.05), eSignificant difference of normal/combined impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance (P<0.05), fSignificant difference of normal/prediabetes (P<0.05), gSignificant difference of normal/diabetes (P<0.05).