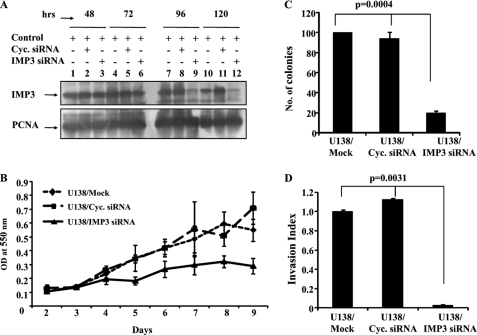
FIGURE 3.
siRNA-mediated IMP3 knockdown in U138 glioma cells reduces proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, and invasion. A, equal amounts of total protein lysates from mock, cyclophilin, and IMP3 siRNA-treated U138 cells at the indicated time points were subjected to Western blotting to detect levels of IMP3 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen proteins. B, viability was measured by MTT assay as an indicator of cell proliferation at the indicated time points for either mock, cyclophilin, or IMP3 siRNA transfected U138 cells. C, U138 cells were either mock, cyclophilin, or IMP3 siRNA-transfected and subjected to soft agar colony formation assay. The number of colonies in the soft agar assay are counted and shown. ANOVA for difference in their colony formation abilities is significant (p = 0.0004). D, the invasion index of either mock, cyclophilin (Cyc.), or IMP3 siRNA-transfected U138 cells was determined based on the BDTM Matrigel assay as per the manufacturer's instructions 24 h after seeding. ANOVA for difference in their invasion index is significant (p = 0.0031).