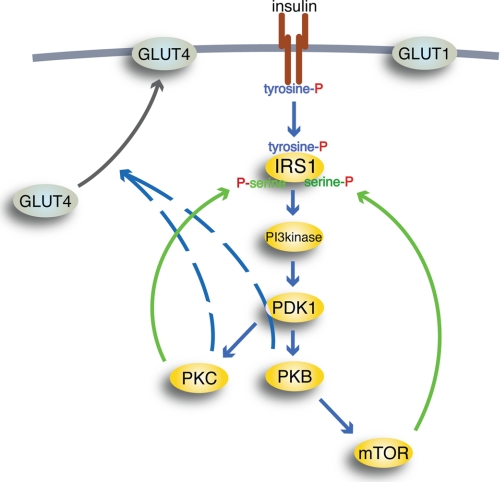
FIGURE 6.
Schematic outline of insulin signaling pathways. Insulin binding to the IR (brown) causes autophosphorylation of IR at tyrosine; thus activated, IR will phosphorylate IRS1 at tyrosine to create binding sites for Src homology 2 domain-containing proteins, such as PI3K (PI3kinase). Thus activated, PI3K will phosphorylate phosphoinositides in the cell membrane, allowing PDK1 to phosphorylate and activate PKB and PKCλ/ζ (PKC). Thus activated, PKB can activate mTOR in complex with raptor, through which insulin can control protein synthesis, autophagy, and mitochondrial function. mTOR and protein kinase PKCλ/ζ relay feedback signals (green) to phosphorylation of IRS1 at serine residues. Blue arrows, downstream signaling by insulin; black arrow, translocation of insulin-regulated GLUT4 from an intracellular location to the plasma membrane (thick gray line); hatched lines, poorly defined signal paths; P, phosphate. GLUT1 is not affected by insulin.