SCHEME 3.
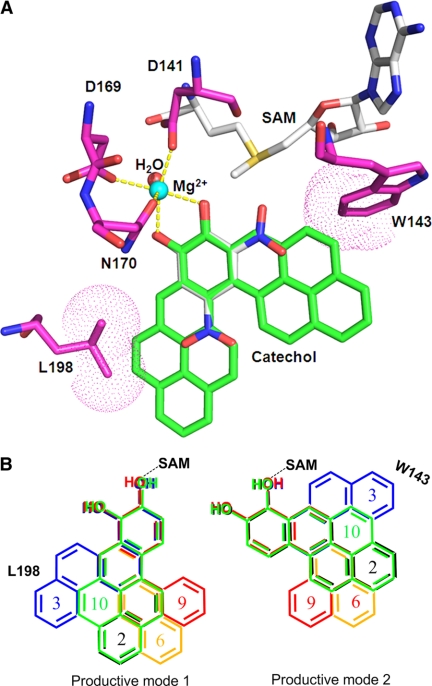
Molecular docking of PAH-catechols in the active site of human COMT. A, human COMT containing 2,5-dinitrocatechol (DNC) and B[a]P-7,8 catechol modeled into the active site. Carbon atoms are colored in green for B[a]P-7,8-catechol, magenta for COMT, and gray for S-adenosyl-l-methionine (AdoMet) and DNC. All the other atoms are color-coded as follows: blue, nitrogen; red, oxygen; yellow, sulfur. Mg2+ and the coordinating water oxygen are shown in cyan and red, respectively. The interactions between the coordinating atoms and the metal ion are indicated by yellow dashed lines. The van der Waals surfaces of the residue atoms interacting with B[a]P-7,8-catechol are shown in dot representations. B, comparison of binding modes of different PAH-catechols. Two productive binding modes are shown (mode 1 and mode 2). The numbers are color-coded with the corresponding PAH ring systems as follows: C-1,2-dione (2, black); C-3,4-dione (3, blue); 7-MBA-3,4-dione (6, orange); B[c]Ph-3,4-dione (9, red); and B[a]P-7,8-dione (10, green). Note that in both binding modes the expanding ring systems of C-3,4-dione are close to residue Leu198 or Trp143, which may account for its low catalytic efficiency. To accommodate C-3,4-dione, both Leu198 and Trp143 must move.