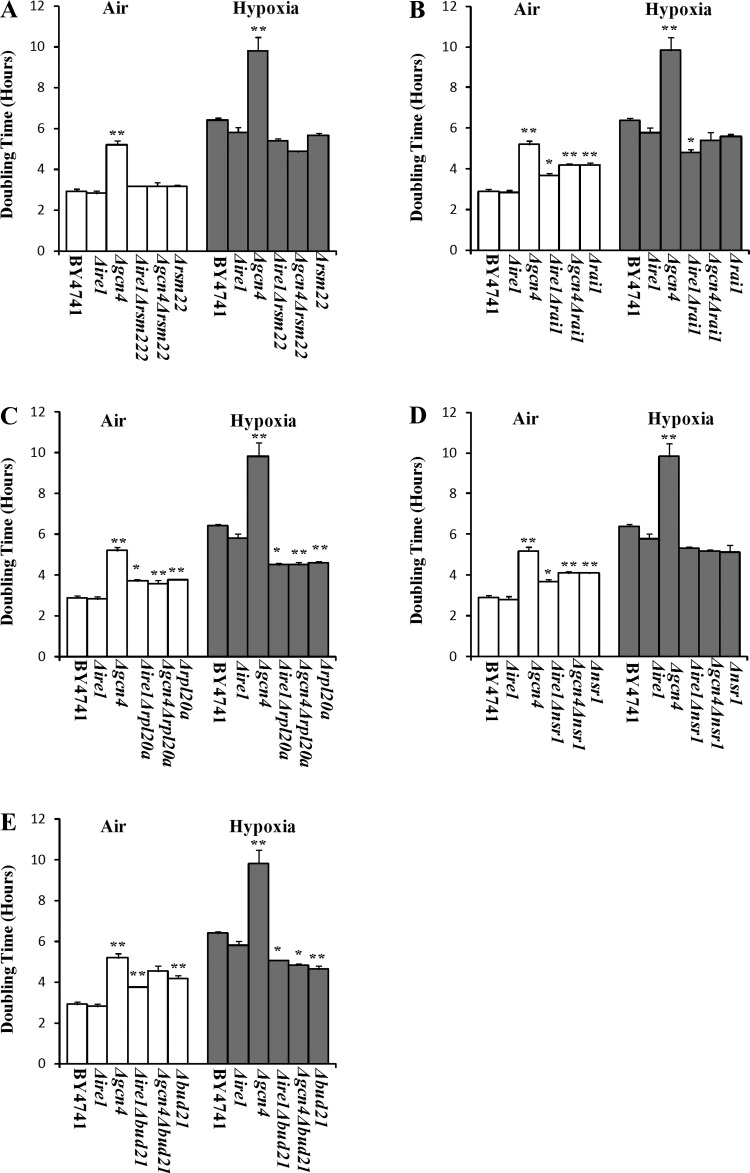
Fig. 6.
The effects of deletion of GCN4 and IRE1 on the doubling times of the wild-type parent and knockout strains with enhanced hypoxia tolerance. A: a comparison of the effect of deletion of GCN4 and IRE1 on the doubling times of the wild-type parent and Δrsm22 strains. B: a comparison of the effect of deletion of GCN4 and IRE1 on the doubling times of the wild-type parent and Δrai1 strains. C: a comparison of the effect of deletion of GCN4 and IRE1 on the doubling times of the wild-type parent and Δrpl20a strains. D: a comparison of the effect of deletion of GCN4 and IRE1 on the doubling times of the wild-type parent and Δnsr1 strains. E: a comparison of the effect of deletion of GCN4 and IRE1 on the doubling times of the wild-type parent and Δbud21 strains. The data plotted here are averages from at least 3 independent cultures. Welch 2-sample t-tests were performed to compare hypoxic with normoxic wild-type or mutant cells. The P values were calculated by using the R program. *P values of < 0.005; **P values of < 0.001.