Fig. 2.
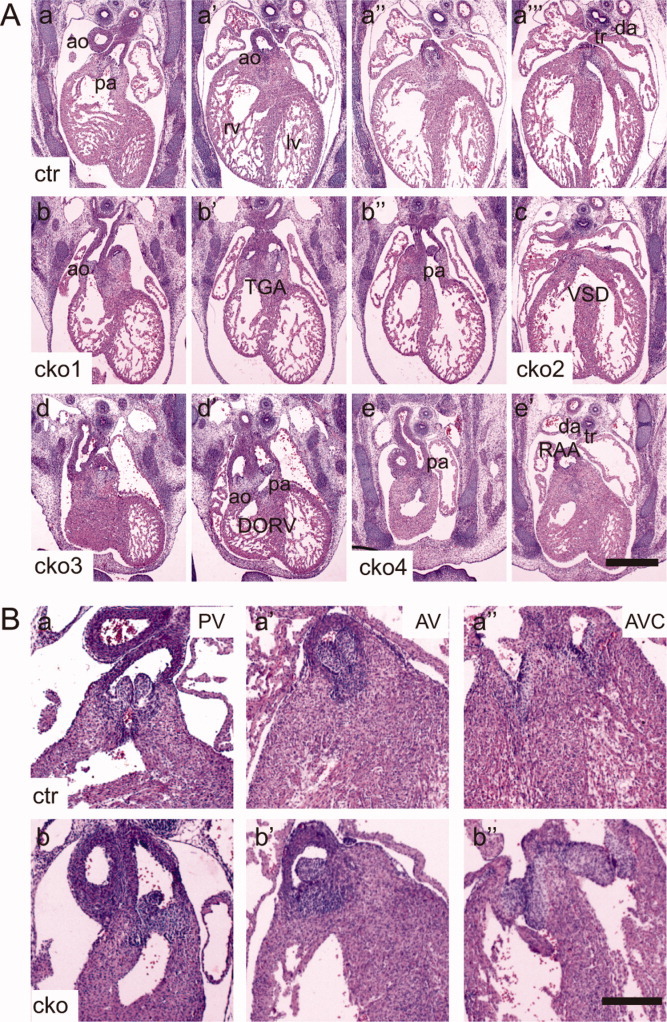
Heart defects in Sur-8Δ/flox;Tie2-Cre embryos. A: Microscopic images showing representative transverse sections from the control (a–a″′) and four Sur-8Δ/flox;Tie2-Cre (b–e′) E13.5 embryos. The images of the sections were arranged from anterior to posterior for each embryo. Note the following heart defects: transposition of the great arteries (TGA, b–b″); ventricular septal defect (VSD, c); double outlets of the right ventricle (DORV, d and d′) and right aortic arch (RAA, e and e′). ao, aorta; pa, pulmonary artery; rv, right ventricle; lv, left ventricle; tr, trachea; da, dorsal aorta. Scale bar = 0.5 mm. B: Images of representative transverse sections from the control and mutant E14.5 embryos. a–a″: Symmetrical outflow tract valves (pulmonary and aortic valves) and mature thinly tapered atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral valves) in the control embryos. b–b″: Outflow tract valve with asymmetrical structure and the underdeveloped atrioventricular valve leaflets in Sur-8Δ/flox;Tie2-Cre hearts. PV, pulmonary valve; AV, aortic valve; AVC, atrioventricular canal. cko, Sur-8Δ/flox;Tie2-Cre; ctr, Sur-8Δ/flox. Scale bar = 0.8 mm.
