Figure 7.
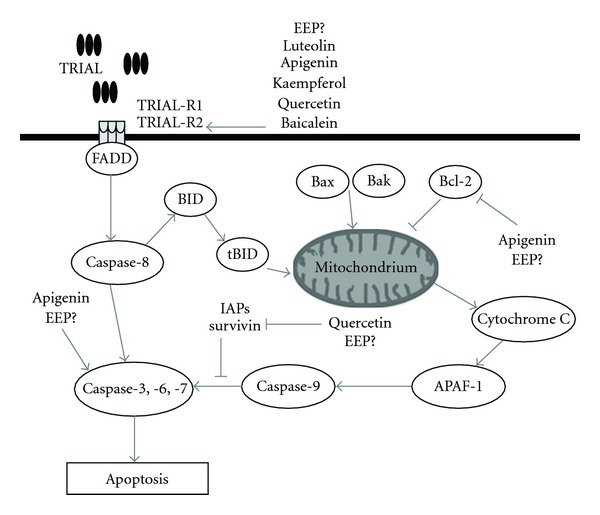
The molecular targets of flavonoids in TRAIL apoptosis pathway and the hypothetic impact of EEP in TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in cancer cell. TRAIL binds to death receptors, TRAIL-R1 and/or TRAIL-R2 and promotes the recruitment of adapter molecule FADD (Fas-associated-death domain) to activate caspase-8, which trigger activation of downstream effector caspases (caspase-3, -6 and -7). Caspase-8 mediated also cleavage of Bid (BH3-interacting domain death agonist). Trucated Bid called tBid translocates to the mitochondria where it interacts with Bax (Bcl-2-associated X protein) and Bak (Bcl-2-agonist/killer), stimulating the release oh cytochrome c. Antiapoptotic members of Bcl-2 family could inhibit cytochrome c release. Cytochrome c liberated from the mitochondria then binds to the adaptor protein APAF-1 (apoptotic protease-activating factor-1) and procaspase-9, forming the apoptosome and activating caspase-9, which in turn activates executioner caspases (caspase-3, -6 and -7) leading to cell death. Caspase-9 activity is controlled by IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis protein) and survivin. Luteolin, apigenin, kaempferol, quercetin and baicalein increase expression of death receptor TRAIL-R2. Apigenin activate executioner caspases and block antiapoptotic Bcl-2 action. Quercetin promotes apoptosis by inhibition of survivin.
