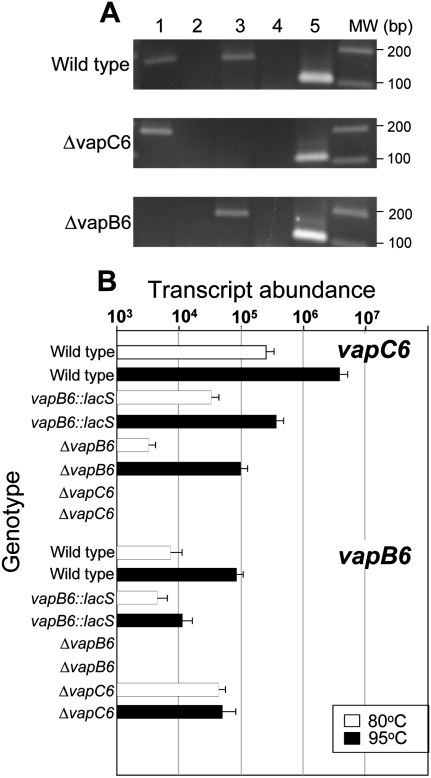
FIGURE 4.
Expression and coupling of vapB6 and vapC6. (A) Detection of vapBC6 transcript. RT–PCR was used to detect transcripts present in wild-type (PBL2025), the vapC6 deletion strain (PBL2080), and the vapB6 deletion strain (PBL2078). (Lanes 1,2) vapB6 transcript with reverse transcriptase (RTase) added or omitted, respectively; (lanes 3,4) vapC6 transcript with RTase added or omitted, respectively; (lane 5) 7S RNA. Location of vapBC6 deleted regions is shown in Figure 1A. (B) Abundance of vapB6 and vapC6 mRNA. qRT–PCR primers used to assess transcript abundance were complementary to regions that remained present in all strains tested. RNA was extracted from cells growing exponentially at the temperatures indicated: (open bars) 80°C; (closed bars) 95°C. Strain genotypes for vapB6 and vapC6, respectively, are indicated across the top of the figure. Strain and relevant vapBC6 genotypes were: + +, wild-type; d +, vapB6::lacS disruption; − +, vapB6 deletion strain; + −, vapC6 deletion. The tbp mRNA was used as an internal control in each RNA sample to normalize vapBC6 values; tbp mRNA varied in abundance by <15% in these experiments.