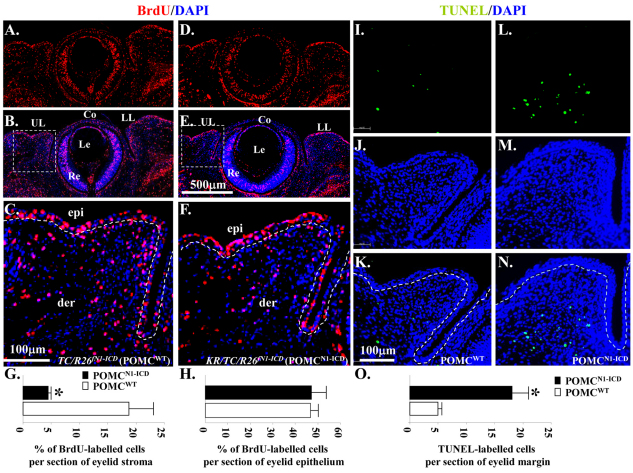
Fig. 5.
Overexpression of N1-ICD decreases BrdU uptake but triggers apoptosis in POMCs during eyelid morphogenesis at E14.5. (A–F) Immunohistochemistry of anti-BrdU antibody. Sections of the eyelids of TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCWT) (A, BrdU; B, BrdU/DAPI merged; C, close-up view from B) and KR/TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCN1-ICD) embryos (D, BrdU; E, BrdU and DAPI merged; F, close-up view from E) labeled with BrdU (red) and nuclear counterstained with DAPI. (I–N) TUNEL assay. Sections of the eyelids of TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCWT) (I, TUNEL; J, DAPI; K, TUNEL and DAPI merged) and KR/TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCN1-ICD) embryos (L, TUNEL; M, DAPI; N, TUNEL and DAPI merged) labeled with Click-iT® TUNEL Assay kit (green) and nuclear counterstained with DAPI. (G) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of BrdU-labeled cells in eyelid stroma. KR/TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCN1-ICD, 4.48±0.45%) embryos showed significant reduction in the percentage of BrdU-labeled eyelid stromal cells, compared with the TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCWT, 18.55±4.34%) littermates in the eyelid mesenchyme. (H) No significant difference of BrdU-labeled eyelid epithelium between POMCN1-ICD (47.54± 7.16%) and POMCWT (46.84±2.84%). (O) Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-labeled cells per section of eyelid margin. KR/TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCN1-ICD, 18.31± 2.49%) embryos showed significant elevation in TUNEL-labeled cells, compared with the TC/R26fN1-ICD (POMCWT, 4.94±0.51%) littermates in the eyelid stromal mesenchyme. Data are represented as mean ± s.d. (n=5). *P<0.05. Dashed lines in C, F, K, and N demarcate eyelid epithelium from stromal mesenchyme. Co, cornea; epi, eyelid epithelium; der, eyelid dermis; Le, lens; LL, lower lid; Re, retina; UL, upper lid.