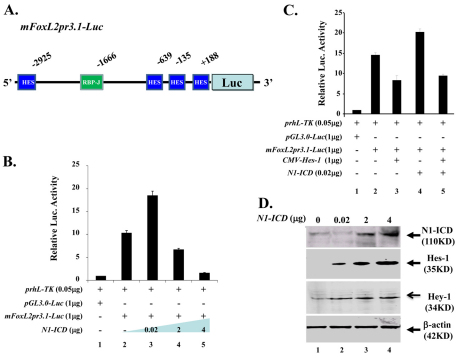
Fig. 9.
Dosage-dependent N1-ICD regulation of FoxL2 promoter activity in vitro. (A) Schematic drawing of mFoxL2pr3.1-Luc vector, which contains one RBP-Jκ site and four potential Hes-1 binding sites in relation to mouse FoxL2 transcription start site (+1). (B) N1-ICD regulates FoxL2 promoter activity. Note that low dose (20 ng) N1-ICD enhances (lane 3) but N1-ICD greater than 2 μg downregulates (lanes 4,5) pGL3.0-mFoxL2pr3.1 promoter activity. (C) Hes1 transcriptional inhibition of pGL3.0-mFoxL2pr3.1 promoter activity (compare lane 3 with lane 2). Note that pGL3.0-mFoxL2pr3.1 promoter activity enhanced by low dose (20ng) N1-ICD is attenuated by co-transfection of CMV-Hes-1 (compare lane 5 with lane 4). (D) Western blotting analysis of Hes-1 and Hey-1 expression in NIH3T3 cells transfected with various amounts of pLIA-mNIC-Myc plasmids. Exogenous N1-ICD upregulates Hes-1 and Hey-1 expression in a dose-dependent manner. Expression level of β-actin serves as a protein loading control.