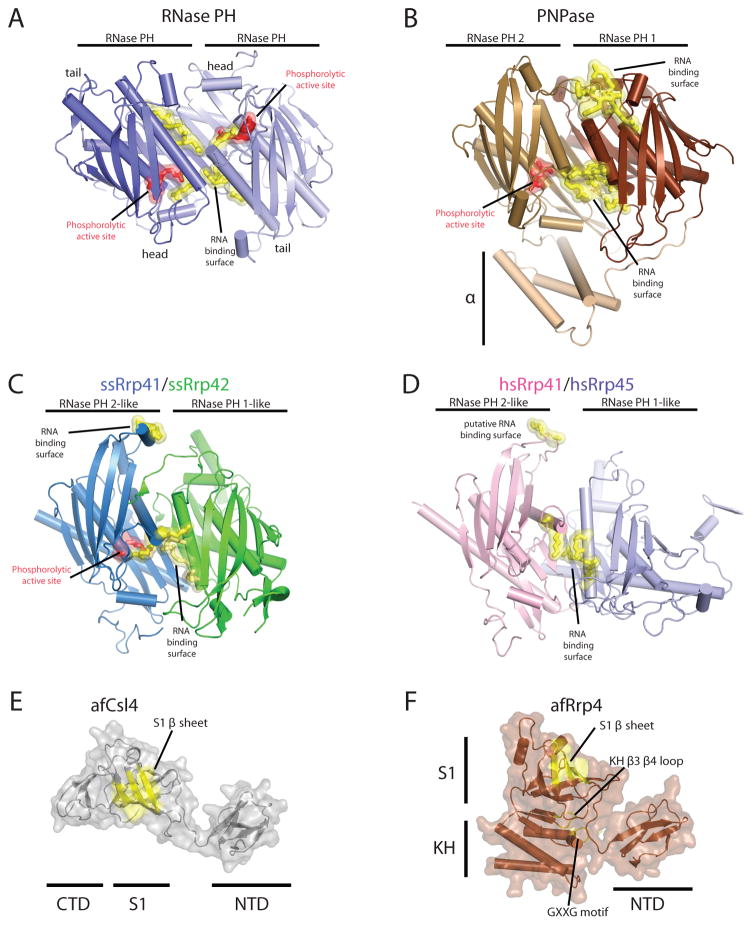
Figure 3. Structures of exosome domains.
Residues in red indicate phosphate binding regions and residues in yellow highlight RNA binding surfaces. Structures depicted in cartoons with helices as tubes and β-strands as arrows. A) RNase PH homodimerization interface (PDB ID = 1UDN). Phosphate binding residues include T125 and R126. RNA binding residues: R86, R92, R96, and R99. B) PNPase RNase PH 1/RNase PH 2 domain binding interface (PDB ID = 1E3P). Phosphate binding residues include: T462 and S463. RNA binding interface residues: R100, R104, R107, R422, and R423. A second RNA binding site includes residues F84, F85, R86, and R87. C) Archaeal S. solfataricus exosome Rrp41/Rrp42 heterodimer interface (PDB ID = 2JE6). Phosphate binding residues are from ssRrp41: S138 and R139. RNA binding interface residues from ssRrp41 are R98 and R99 and R112, R116, and R119 (ssRrp42). The second RNA binding region includes residues R67 and H68 (from ssRrp41) D) Eukaryotic H. sapiens Rrp41/Rrp45 hetero-dimerization interface. Putative RNA binding interface residues include: K94, S95, R104, R108, and R111, and the second putative RNA binding region includes residues R61 and A62. Structures for the archaeal three-component cap subunits (PDB ID = 2BAO and 2BA1): E) A. fulgidus Csl4 and F) A. fulgidus Rrp4. Putative RNA binding surfaces are highlighted in yellow for the S1 domain and KH domain on a transparent surface representation. Similar structures exist for the human three-component cap subunits Csl4, Rrp4 and Rrp40 as discussed in the text (PDB ID = 2NN6).