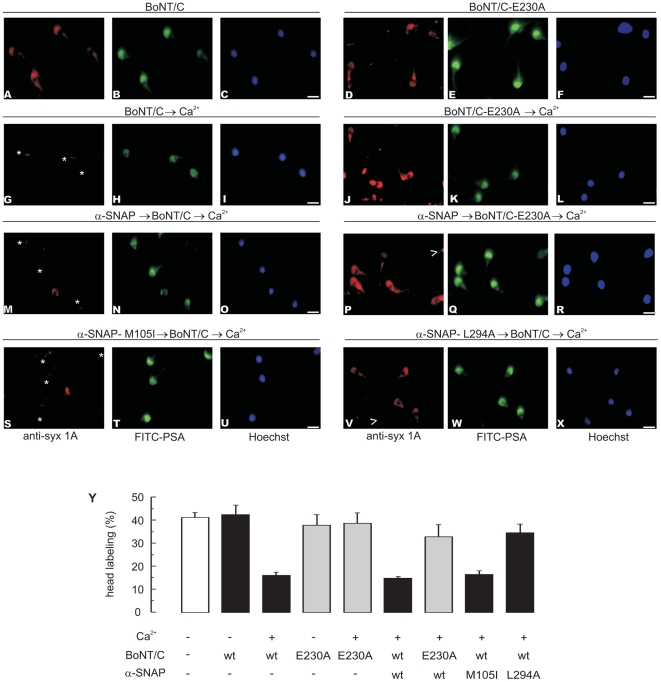
Figure 5. α-SNAP does not interfere with sperm SNARE complex disassembly.
Permeabilized spermatozoa were loaded for 15 min at 37°C with 300 nM α-SNAP wild type (M, N, O), 50 nM α-SNAP-M105I (S, T, U), or 400 nM α-SNAP-L294A (V, W, X), subsequently treated with 100 nM BoNT/C and finally activated with 0.5 mM CaCl2. The cells were then fixed and triple stained with the rabbit polyclonal anti-syntaxin1A antibody (that recognizes an epitope located in a portion of the molecule released by the toxin; “anti-syx 1A”, red, left panels), FITC-PSA (to differentiate between reacted and intact sperm; green, central panels), and Hoechst 33342 (to visualize all cells in the field; blue, right panels). Notice that reacted sperm were negative for syntaxin1A staining (arrowheads in panels P and V). Asterisks in panels G, M and S indicate cells with intact acrosomes but without syntaxin1 immunostaining due to toxin cleavage. BoNT/C had no effect on syntaxin1A staining in resting sperm (A). Labeling in sperm stimulated with calcium was significantly reduced by the wild type (G) but not by the catalytically dead (J, P) BoNT/C. Bars = 5 µm. Y, Quantification of the percentage of cells exhibiting syntaxin1 acrosomal staining from three independent experiments (mean ± S.E.M.).