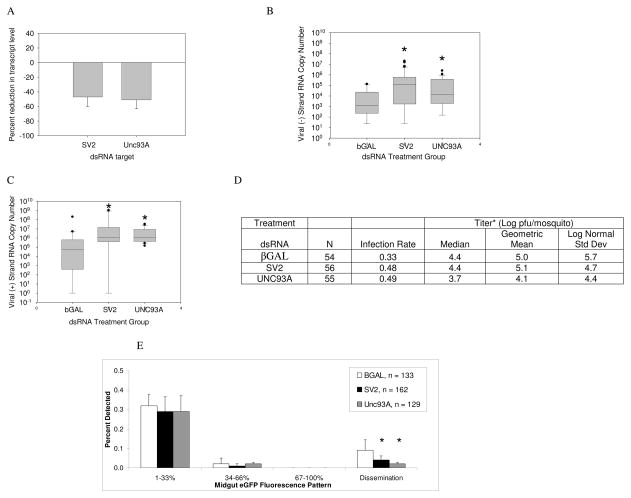
Figure 3.
Viral RNA accumulates in UNC93A and SV2-silenced mosquitoes over βGAL-injected controls, but dissemination is reduced. (A) Evidence of gene silencing. Mosquitoes were injected with dsRNA immediately following a virus blood meal, and at 4 dpi, transcripts were detected using qRT-PCR. Relative transcript levels were normalized to an RPS7 reference standard and those of βGAL injected controls to calculate percent reduction. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean of three independent experiments. (B) Negative strand viral RNA copy number per mosquito. Levels are statistically significant difference from control per Mann-Whitney U Test (SV2, p=0.002; UNC93A, p=0.02). (C) Positive strand viral RNA copy number per mosquito. Mosquitoes were harvested at 4 dpi and subjected to two step qRT-PCR, (SV2, p=0.02; UNC93A, p=0.02). The data are representative of at least three biological replicates. Box outline displays 75th and 25th percentiles, while the whiskers show the 90th and 10th percentiles. (D) MRE16-eGFP virus production. *, Titer median and geometric means were calculated from infected mosquitoes. (E) Percentage of cells expressing eGFP is significantly reduced in both UNC93A- and SV2-silenced mosquitoes. Mosquitoes were harvested at 4 dpi and subjected to fluorescence microscopy at a 488nm excitation wavelength. Midgut infections were classified by the percentage of expressing eGFP. “Dissemination” refers to the percentage of mosquitoes displaying fluorescence in peripheral tissues. The data are representative of at least three biological replicates. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Mann-Whitney test (p<0.05).