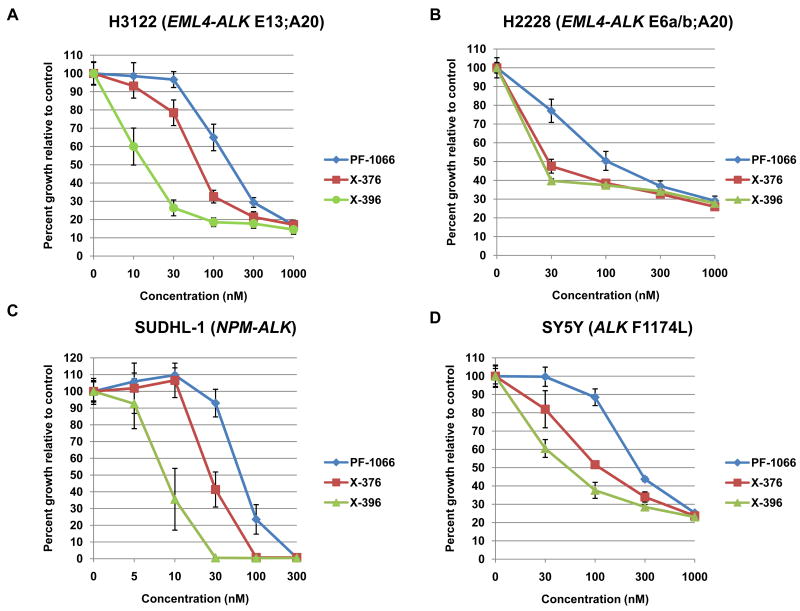
Figure 2. Potency of X-376 and X-396 in ALK mutant cell lines.
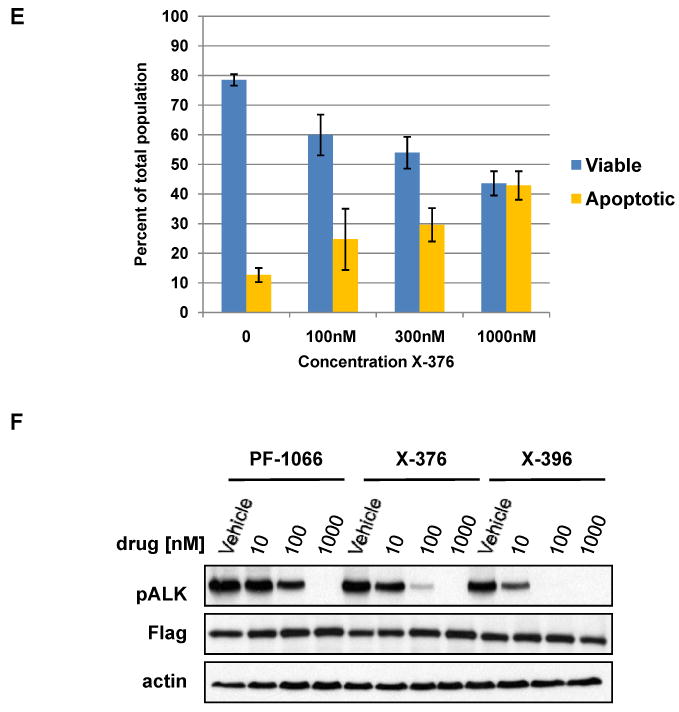
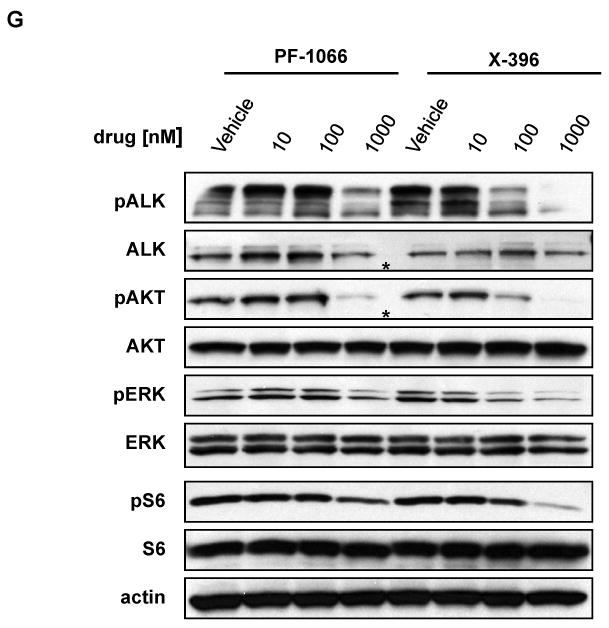
(A-D) H3122 lung cancer cells containing the EML4-ALK E13;A20 fusion, H2228 lung cancer cells harboring the EML4-ALK E6a/b;A20 fusion, SUDHL-1 lymphoma cells containing NPM-ALK fusion, and SY5Y neuroblastoma cells with an activating mutation within the ALK kinase domain (ALK F1174L) were treated with ALK TKIs or vehicle for 72h. Cell titer blue assays were performed to assess growth inhibition. Each point represents hextuplicate replicates. Data are presented as the percentage of viable cells compared to control (vehicle only treated) cells. See methods for details. (E) Apoptosis is induced by X-376 treatment. H3122 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of X-376 for 72h. Cells were stained with annexin V (AV) and propidium iodide (PI) and counted on a FACSCanto II machine. Viable cells are defined as the AV/PI double negative population. Apoptotic cells are defined as the sum of AV positive, PI negative plus AV/PI double positive cell populations. (F) 293 cells were transiently transfected with 3Flag-EML4-ALK E13;A20. At 48 hours post transfection, the cells were treated with increasing amounts of the ALK TKIs for 2 hours. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies specific for the indicated proteins. (G) H3122 lung cancer cells containing the EML4-ALK E13;A20 fusion were treated with increasing amounts of ALK TKIs for 1 hour as indicated. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the specified antibodies. The asterisks (*) in the ALK and phospho-AKT blot indicate an empty lane (no lysate loaded) on the gel.