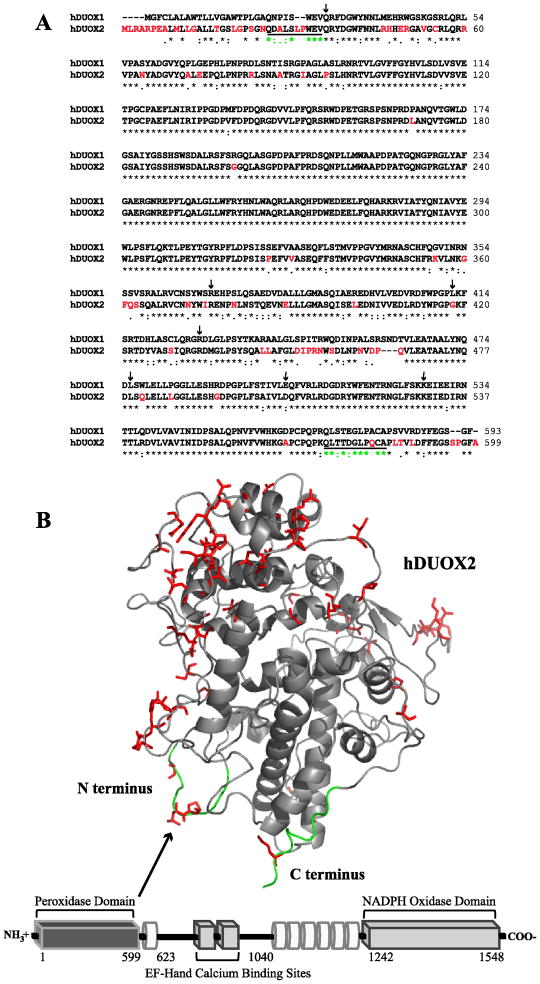
Figure 1.
Sequence and structural features of hDUOX2. (A) Sequence alignment of the peroxidase domains of hDUOX1 and 2 (hDUOX11–593 and hDUOX21–599). Amino acids which differ significantly (1dot or no symbol designation) between the two proteins have been highlighted in red, corresponding with the model structure of hDUOX21–599. Residues defined as the N and C termini of the hDUOX2 model structure are underlined. Amino acids subject to disease related mutations in hDUOX2 are highlighted by arrows (Q36H, R376W, G418fsX482, R434X, L479SfsX2, D506N, K530X). (B) Bottom: Schematic view of the domain structure of hDUOX2. Each DUOX protein contains an N-terminal extracellular “peroxidase” domain (dark gray rectangle), putative TM domains (white tubes) which bind two heme molecules, and cytosolic EF-hand and NADPH oxidase domains (light gray rectangle). hDUOX2 was truncated to generate a soluble expression construct limited to the peroxidase domain, as highlighted by the model structure (Top). Residues of greatest amino acid difference between hDUOX isoforms are highlighted in red and shown as sticks; the N and C termini of the hDUOX21–599 model structure are highlighted in green.