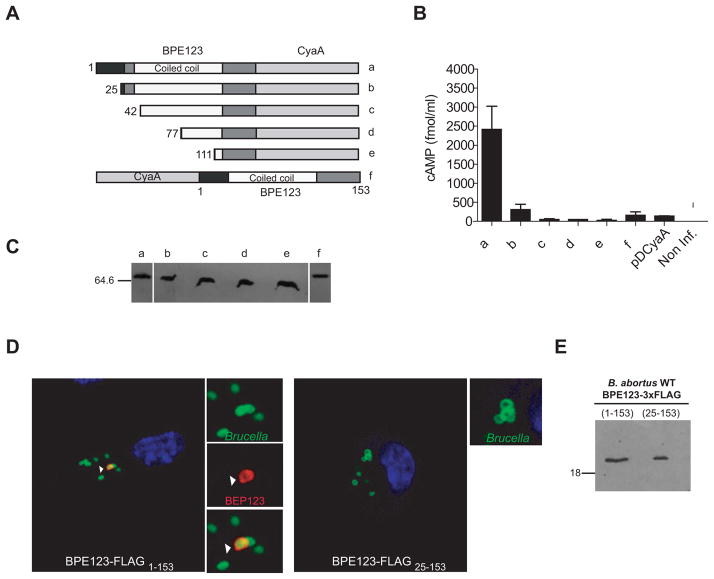
Figure 5. The N-terminal 25 amino acids of BPE123 are essential for translocation into host cells.
(A and B) J774.A1 cells were infected with B. abortus strains expressing full length and N-terminal truncations of BPE123-CyaA (a–e) as well as CyaA-BPE123 hybrid protein (f). Protein translocation was measured by determining the intracellular cAMP levels in J774.A1 cells infected for 5 h with B. abortus strains harboring the indicated plasmids. The wild type strain (2308) expressing the CyaA domain alone (pDCyaA) was included as a control. Intracellular cAMP was also quantified in non-infected cells. Mean and SD are shown for one representative out of three independent experiments. (C) Full length and N-terminal truncations of BPE123-CyaA (a–e) as well as CyaA-BPE123 (f) hybrid protein levels were determined by immunoblot analysis with anti-CyaA antibodies. (D) Representative confocal micrographs of mouse BMDM infected with wild-type B. abortus expressing full length (left panel) or truncated (right panel) BPE123-3xFLAG (MOI 20:1). At 5 h p.i. cells were fixed and processed for immunostaining as described in materials and methods. Arrows indicate the location of full length BPE123 in the proximity of a BCV. (D) Full length (lane 1) or truncated (lane 2) BPE123-3xFLAG protein levels of the indicated B. abortus strains were determined by immunoblot analysis with anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody.