Figure 2.
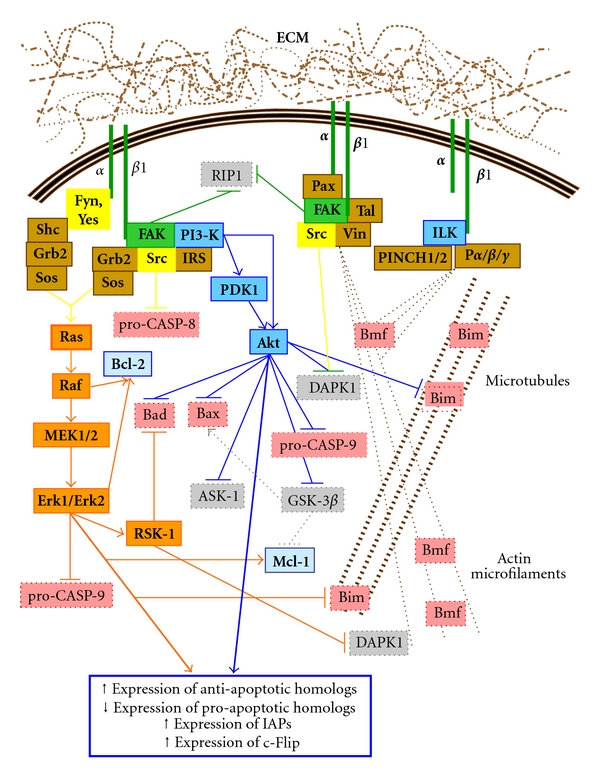
β1/Fak/Src integrin signaling, cell survival, and suppression of anoikis. Binding of an (α)β1 integrin to its ECM ligand primarily allows the recruitment and activation of Fak. On the one hand, Fak activates PI3-K directly or indirectly via Src and/or an IRS, leading to activation of Akt. Activated Akt then performs various cell survival functions. On the other hand, Fak may directly recruit Grb2-Sos, or indirectly via Src, leading to the activation of the small GTPase Ras and thereby stimulating the Raf/MEK/Erk pathway. This latter pathway can also be stimulated by certain partner α subunits of β1, through the recruitment/activation of Fyn or Yes, two other Src family members, and their subsequent recruitment of p52Shc-Grb2-Sos. The Raf/MEK/Erk pathway then likewise performs cell survival functions. Additionally, the stimulation of the PI3-K/Akt and/or Raf/MEK/Erk pathways generally results in an upregulation of Bcl-2 expression for the anti-apoptotic homologs and a down-regulation for the pro-apoptotic homologs, as well as an upregulation of IAP expression and other apoptosis suppressor molecules, such as c-Flip. Alternatively, Fak and/or Src will participate in the recruitment of paxillin, talin, vinculin to assemble focal adhesions in direct association with actin microfilaments. Similarly, ILK will be engaged by β1 integrins to assemble and regulate focal adhesions along with its PINCH and parvin partners, whereas ILK can also contribute in microtubule assembly/stability. The overall stabilization of the cytoskeleton enables the sequestration of the pro-apoptotic homologs Bmf and Bim. Note that various other survival signaling pathways stimulated by integrin β1/Fak/Src signaling (e.g., p130CAS-Nck-PAK, and PKC) are not shown here for reasons of clarity and conciseness. Pα/β/γ, parvin α, β, γ; Pax, paxillin; PINCH1/2, particularly interesting new cysteine-histidine rich protein-1/-2; Tal, talin; Vin, vinculin.
