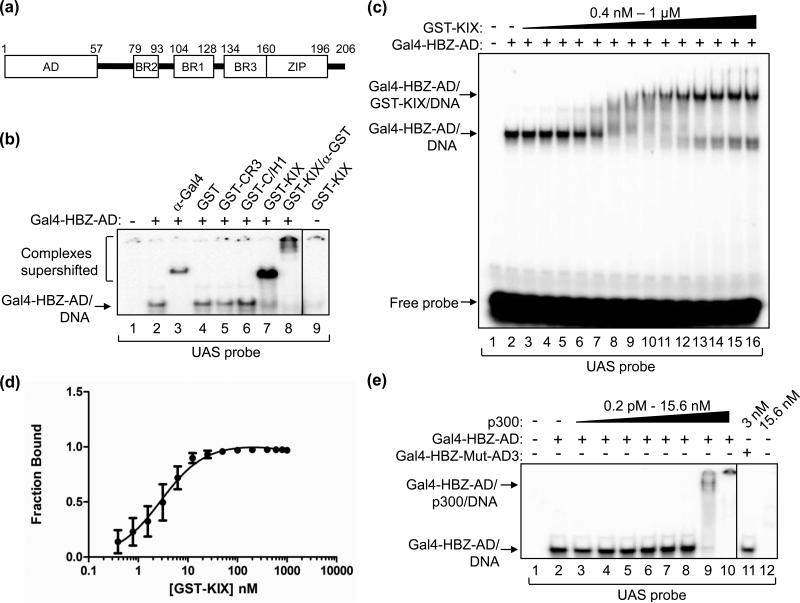
Figure 1. HBZ-AD displays high affinity-binding to the KIX domain of p300/CBP.
(a) The schematic representation of HBZ shows the N-terminal activation domain (AD), three basic regions (BR2, BR1 and BR3) and the C-terminal leucine zipper (ZIP). (b) Gal4-HBZ-AD interacts specifically with the KIX domain. EMSA reactions contained the UAS DNA probe (5 nM) and, where indicated, Gal4-HBZ-AD (1 nM). Reactions were supplemented with either anti-Gal4-DBD antibody (5 ng), GST (50 nM), GST-CR3 (50 nM), GST-C/H1 (50 nM), GST-KIX (50 nM) or anti-GST antibody (3.1 μg) as indicated. (c) EMSAs were used to determine the apparent Kd for the Gal4-HBZ-AD:GST-KIX complex. Reactions contained UAS probe (2.5 nM), Gal4-HBZ-AD (1 nM; lanes 2-16) and increasing concentrations of GST-KIX (0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000 nM; lanes 3-16). (d) The binding curve, generated by nonlinear regression analysis, yields an apparent Kd of 3 ± 0.5 nM. The graph shows the fraction of Gal4-HBZ-AD bound to GST-KIX versus the concentration of GST-KIX (nM) as determined by quantification of three independent EMSAs. (E) Gal4-HBZ-AD binds strongly to full-length p300. EMSA reactions contained UAS probe (2.5 nM), Gal4-HBZ-AD (2.5 nM; lanes 2-10) and increasing concentrations of p300 (0.2 pM, 1 pM, 5 pM, 25 pM, 125 pM, 625 pM, 3 nM, and 15.6 nM; lanes 3-10). Lane 11 contained Gal4-HBZ-Mut-AD3 (2.5 nM) and p300 (3 nM); lane 12 contained only p300 (15.6 nM) and the UAS probe. Lanes shown are from the same gel. Vertical lines show where the gel was cropped.