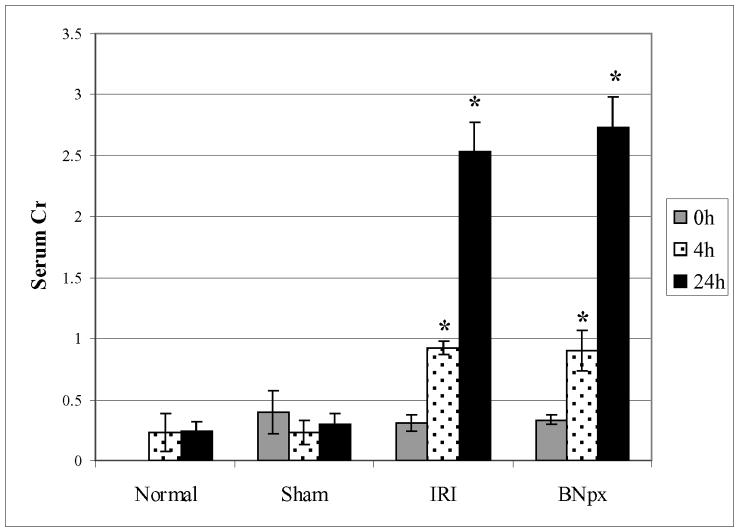
Figure 1. Experimental AKI Leads to Renal Injury.
Prior to endothelial cell isolation, mice underwent 60 minutes of bilateral IRI, bilateral nephrectomy or sham surgery, and were then sacrificed at either 4 or 24 hours post-procedure. Normal mice (without any surgical intervention) were also sacrificed at the final time point as internal controls. Serum creatinines were measured prior to surgery (0h) and at time of sacrifice (4h or 24h). Both bilateral IRI and nephrectomy result in significant renal injury (*) while sham surgery does not increase creatinine levels above normal baseline. There was no significant difference between the rise in serum creatinine induced by IRI sersus bilateral nephrectomy. Results shown are average serum creatinine values for a representative experiment with error bar signifying standard deviation (n=5 mice per group).