Fig. 2.
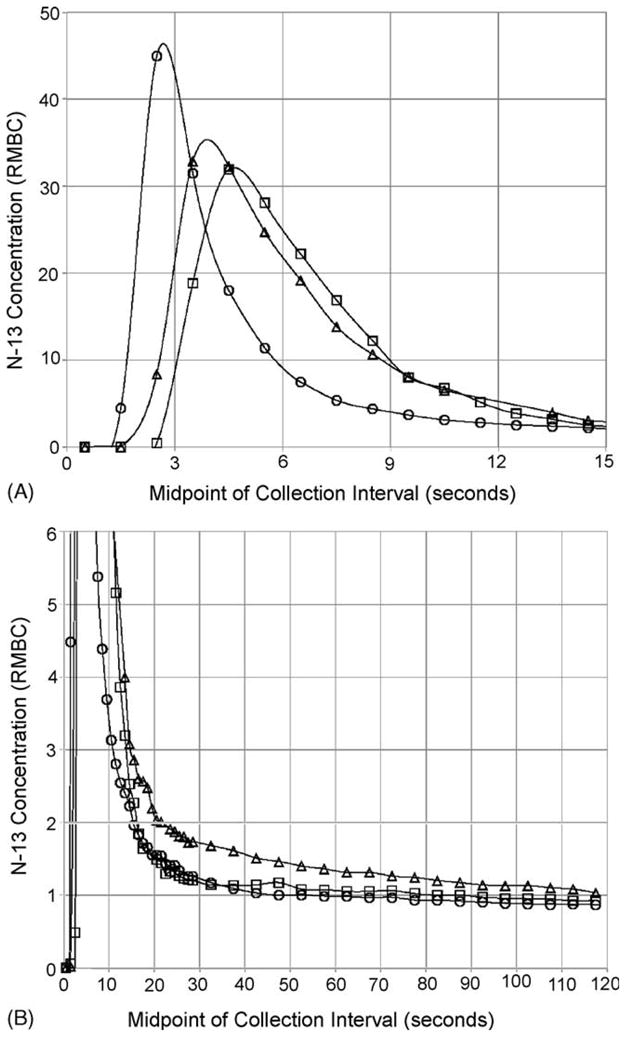
Concentration (RMBC) of 13N activity in arterial rat blood versus time after injection. A bolus (0.3–0.4 ml) of [13N]ammonia solution was injected into the femoral vein of each of three anesthetized 250 g rats and blood samples were collected from a cannula in the tail artery every second for 30 s and every 5 s thereafter for the next 90 s. Using a distinct symbol for each rat, RMBC measurements are plotted against time (the midpoint of each collection interval). (A) and (B) show the measurements for the first 15 s and the first 2 min, respectively. Smoothed curves have been fitted through the data points for each rat. RMBC is “the ratio to mean body concentration” and is defined as the decay-corrected fraction of injected tracer recovered in a specimen divided by the fraction of body weight contained in that specimen. From Freed and Cooper (2005) with permission.
