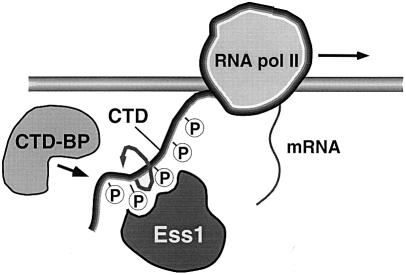
Fig. 7. Model for the action of Ess1 in transcription. Ess1 binds the phosphorylated CTD of RNA pol II, catalyzing its isomerization, thus acting as a regulatory switch for loading of proteins required for initiation, elongation, termination and 3′ end formation. In this model, Ess1 coordinates the sequential steps of transcription by changing the three-dimensional structure of the CTD, altering the affinity of protein–CTD interactions. Binding of Ess1 to the CTD would be regulated by phosphorylation–dephosphorylation by CTD kinases and CTD phosphatases (e.g. Fcp1). Ess1 might instead work stoichiometrically; Ess1 would sterically block (or promote) binding of RNA pol II-associated proteins to the phosphorylated CTD.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.