Figure 2.
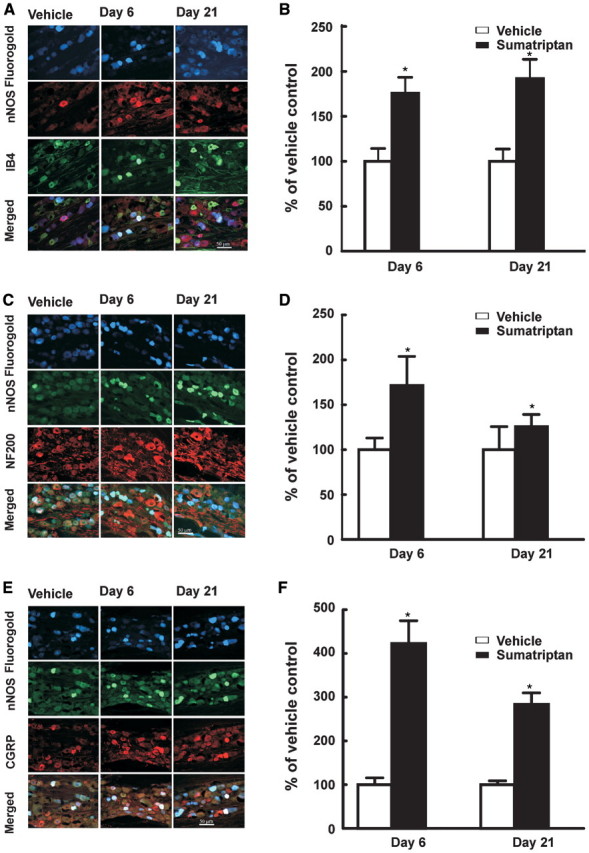
Sustained infusion of sumatriptan lead to an increased expression of neuronal NOS (nNOS) in normally ‘peptide-poor’ unmyelinated fibres and in myelinated fibres. Dural afferents were identified by administration of Fluorogold to the dura 4 days prior to collecting trigeminal tissue for immunofluorescent imaging. Trigeminal ganglion sections were obtained from rats 6 and 21 days after initiation of sumatriptan infusion (0.6 mg/kg/day, s.c.) and labelled for neuronal NOS. The sections were also labelled for reactivity to IB4 (A, B) or NF200 (C, D). The proportion of retrogradely-labelled profiles also showing label for neuronal NOS and for either IB4 or NF200 were determined relative to that shown by sections obtained from saline-treated rats. Sumatriptan infusion resulted in significant (P < 0.05) increase in retrogradely-labelled trigeminal profiles expressing label for neuronal NOS and either IB4 (B) or NF200 (D) 6 and 21 days after initiation of infusion. In dural afferents of the trigeminal ganglia, exposure to sumatriptan increased the co-expression of neuronal NOS with CGRP in retrogradely-labelled trigeminal profiles. After retrolabelling the dural afferent of the trigeminal ganglia, sections were prepared for fluorescent staining to visualize CGRP and neuronal NOS at Day 6 and 21 after sumatriptan exposure (E). The numbers of profiles expressing neuronal NOS and CGRP were counted (F). Sumatriptan exposure induced a marked significant (P < 0.05) increase in co-expression, relative to vehicle-infused animals, 6 and 21 days after sumatriptan pump implantation. Asterisk indicates P < 0.05 relative to vehicle.
