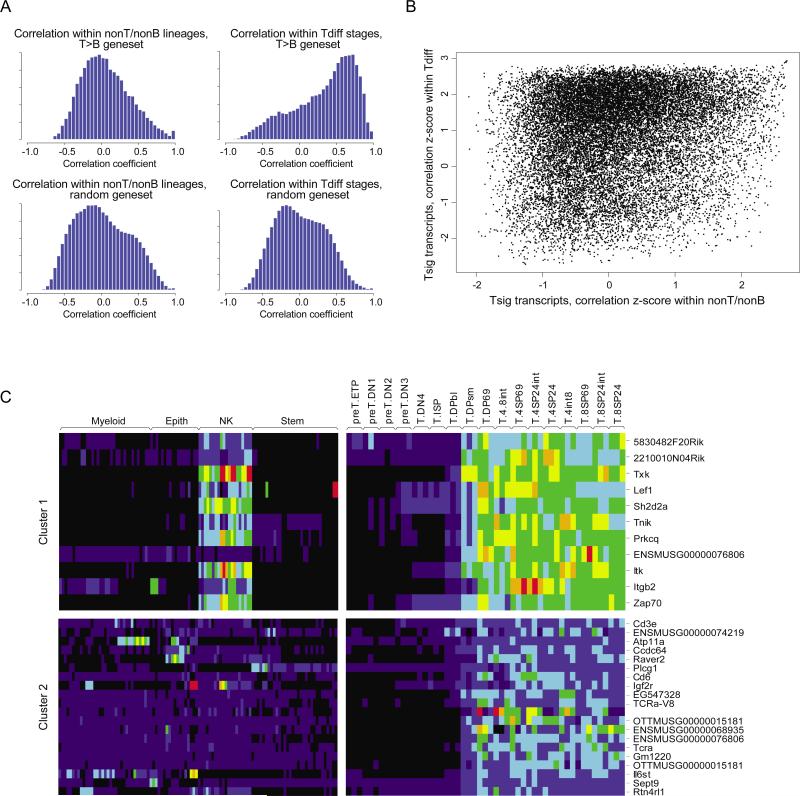
Figure 5. Partial sharing of co-regulated gene clusters within T cell differentiation and outside the T cell lineage.
To determine which transcripts exhibit coordinated expression, as a reflection of possible shared regulatory mechanisms, pair-wise correlation coefficients were calculated for all transcripts of the “Top 200” T cell signature genes, within all ImmGen datasets except for T and B cells (“nonT/nonB”) or within the T cell differentiation datasets. As a reference, the same coefficients were calculated on a set of 2000 transcripts picked at random. A): distribution of the correlation coefficients; note that there is a very significant skewing of the distribution of correlation coefficients between T signature genes in the T-differentiation datagroup (top left), far less marked within the nonT/nonB datagroup (top right). B): Scatter plot comparison of all pair-wise correlations between T signature genes within the nonT/nonB (X-axis) or T-differentiation (Y-axis) datagroups; to avoid artifacts due to the different sizes and composition of the nonT/nonB and T-differentiation datasets, the primary correlation coefficients were transformed to a z-score by reference to the mean and standard deviation of the correlation coefficients for the randomly picked reference gene-set. Note that the majority of transcript pairs that show strong correlation within the T-differentiation datagroup (z-score > 2) show no correlation within the nonT/nonB populations (z-scores distributed around 0), although there is a distinct “shoulder” of gene pairs that do show some correlation across both conditions (top right of the plot). C): A k-means clustering algorithm was used to partition T-signature genes into distinct clusters based on their correlation within the T-differentiation datagroup. Transcript levels for representative clusters are shown as a heat-map for the nonT/nonB (left) and T-differentiation (right) datagroups. A few clusters showed consistent expression across both datagroups (e.g. Cluster 1, top, primarily reflecting shared expression with NK cells), while many were only co-regulated within the T-differentiation datagroup.