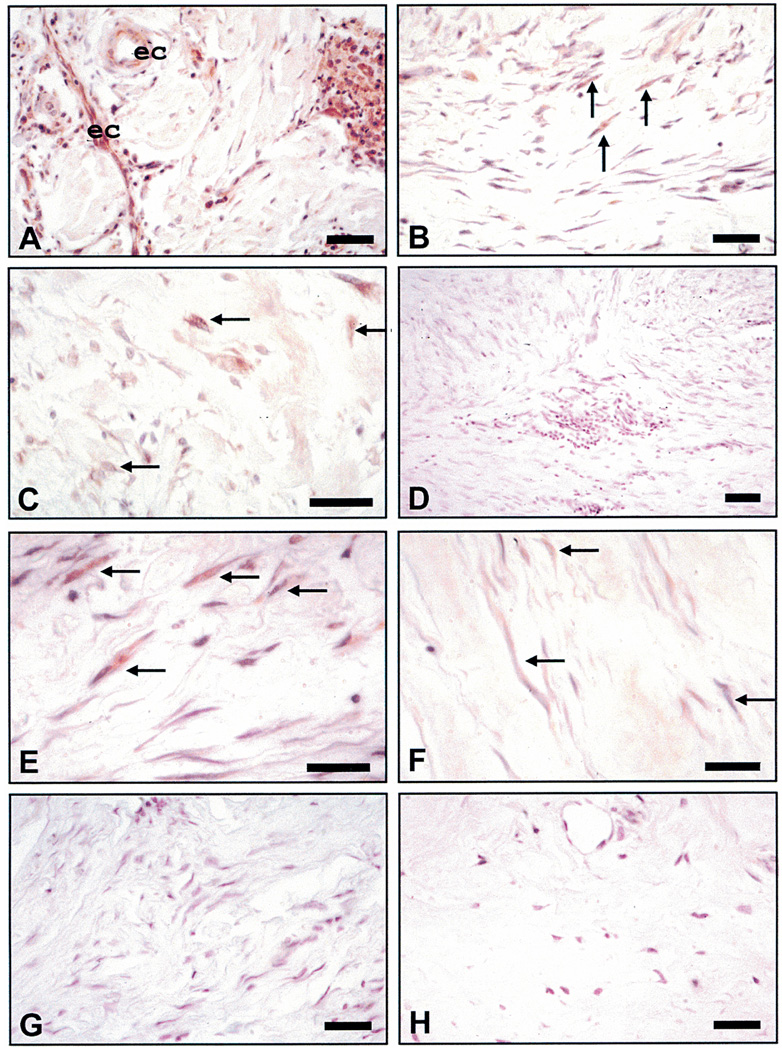
Figure 2.
Immunohistochemical staining for CXCR2. (A) Keloid showing intensive immunoreactivity for receptor in endothelial cells (ec) and inflammatory infiltrates (arrows). (B) A keloid showing immunoreactivity for receptor in multiple myofibroblasts. (C) A keloid showing moderate immunoreactivity for the receptor in only a few of the fibroblasts/myofibroblasts (arrows). (D) A keloid exhibiting little or no evidence that the receptor is expressed. (E) A keloid showing robust immunoreactivity in cells with a fibroblastic/myofibroblastic phenotype. (F) A keloid showing minimal immunoreactivity in the fibroblast population (arrows). (G) A representative hypertrophic scar showing minimal to no staining for the receptor. (H) Normal skin from an equivalent area of deep dermis showing no immunoreactivity for CXCR2 in dermal cell population. All size bars indicate 50 µm.