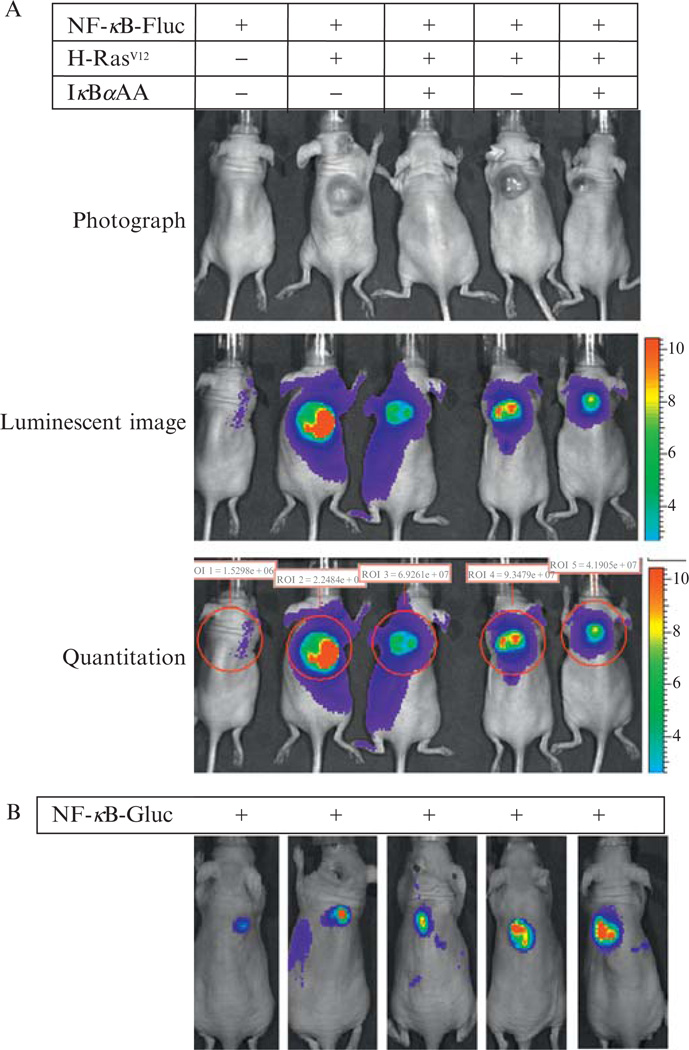
Figure 17.1.
Intratumoral NF-κB reporter models. (A) NF-κB-Fluc reporter model. Mouse melanocytes null for INK4A/ARF were genetically engineered with the NF-κB-Fluc reporter (lanes 1to 5),CMVpromoter^driven oncogenic H-RASV12 expression (lanes 2 to 5), and/or a Tet-On inducible IkBa(S32A/S36A) superrepressor expression vector (lanes 3 and 5).These cellswere inoculated into nudemice to develop xenografts. Tumors were photographed (upper panels) and intratumoral NF-κB activities were determined by quantitative luminescent imaging (lower panels), illustrating that H-RASV12 inducedNF-κBactivation in vivowas inhibitedwith the IκBα superrepressor. (B) NF-κB-Gluc reporter model. NF-κB-Gluc was stably expressed in human melanoma Hs294Tcells (1 × 106) and these cells were subcutaneously inoculated into nude mice. The individual bioluminescent image was taken immediately following intravenously injection of 100 µg native coelenterazine per mouse.