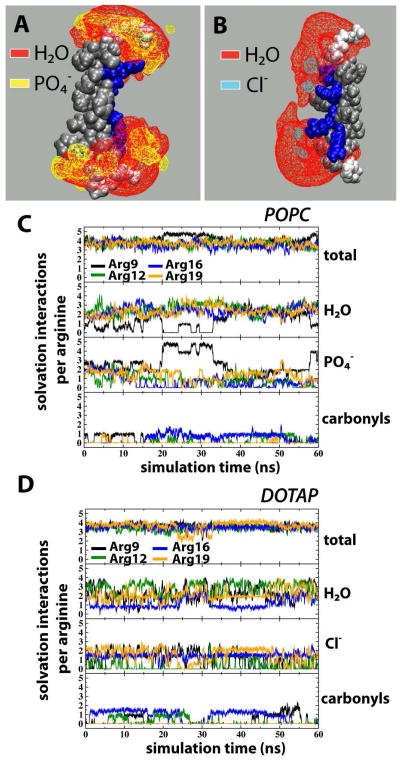
Figure 4.
Isosurfaces and solvation-interaction counts for S4mut (2-up-2-down) in POPC and DOTAP bilayers. (A) Isosurfaces of lipid phosphates (yellow) and water molecules (red) based on 60 ns equilibrated simulation of S4mut in POPC. (B) Isosurfaces of water molecules (red) and chloride counterions (cyan) based on 60 ns equilibrated simulation of S4mut in DOTAP. For clarity, the isosurfaces are depicted at 10% occupancy. (C) The total number of solvation interactions (first panel), the number of water H-bonds (second panel), the number of lipid phosphate interactions (third panel), and the number of H-bonds to the lipid carbonyl oxygens (fourth panel), formed by the S4mut helix in POPC. (D) The total number of solvation interactions (upper panel), the number of water H-bonds (second panel), the chloride ion interactions (third panel), and the number of H-bonds to the lipid carbonyl oxygens (fourth panel), formed by S4mut helix in DOTAP. The criteria for the presence of a solvation interaction were defined by cut-off values; 3.5 Å for the distance and 40 degrees for the angle.